pH meter is used to measure the acidity and alkalinity of a solution by measuring Hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. pH Meter Calibration is required at regular intervals or as per the defined frequency to maintain its accuracy. Here, we will discuss the pH meter principle, ph meter electrode, Range of pH, Calibration, Key components or parts of the pH instrument, Working, precautions, Advantages, and Disadvantages.
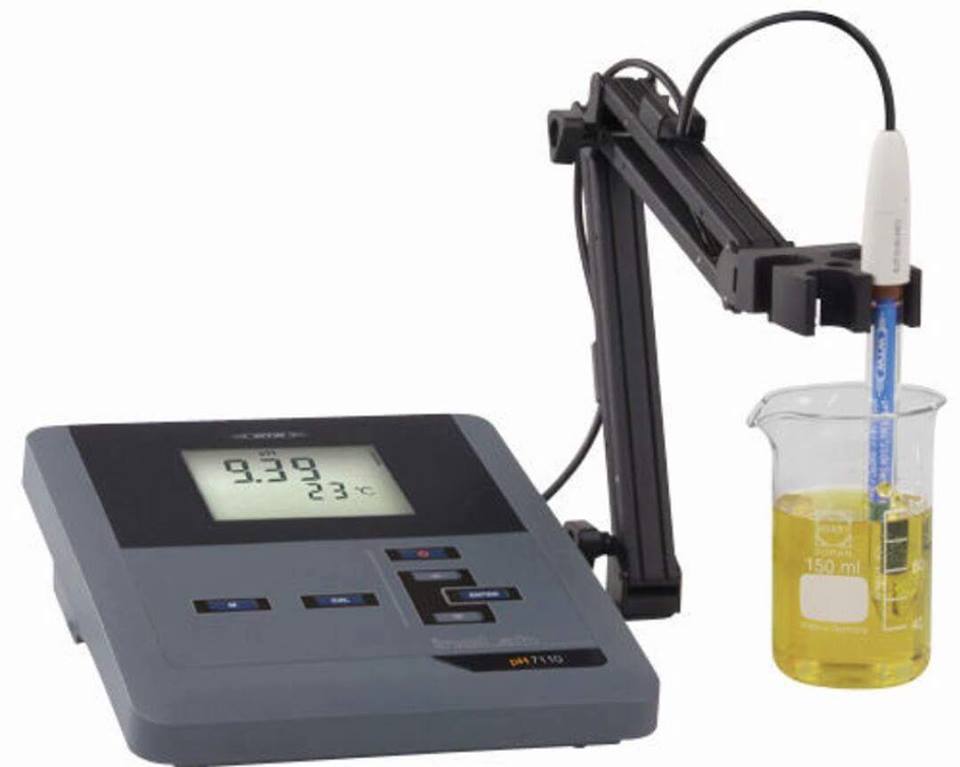

pH Meter Principle
pH Meter Principle: It measures the voltage between the two electrodes, one is a glass electrode, and the other is a reference electrode. Sometimes, if both electrons are present, it is called the combination electrode, and they are inserted into the solution in which pH is to be tested, after immersing these electrodes in a solution, the H+ ion in the test solution was exchanged for other positively charged hydrogen ions present on the glass ball. So there is an action between these H+ ions of the solution and the H+ions or positively charged ions present in the glass bulb. The amplifier detects the difference in electric potential between the two electrodes. The contrast of these potentials is called the ph unit.
Why Range of pH always lie between 1 to14
pH is always measured between (1 to14). The solution having pH=1 is called an acidic solution, or generally, it is highly acidic. The solution with the pH=14 is highly alkaline, or it is a more natural solution than the solutions having more H+ ion concentration. It is highly acidic, and the solutions with more OH– ions are highly basic or highly alkaline.
Key Components or parts of pH instrument
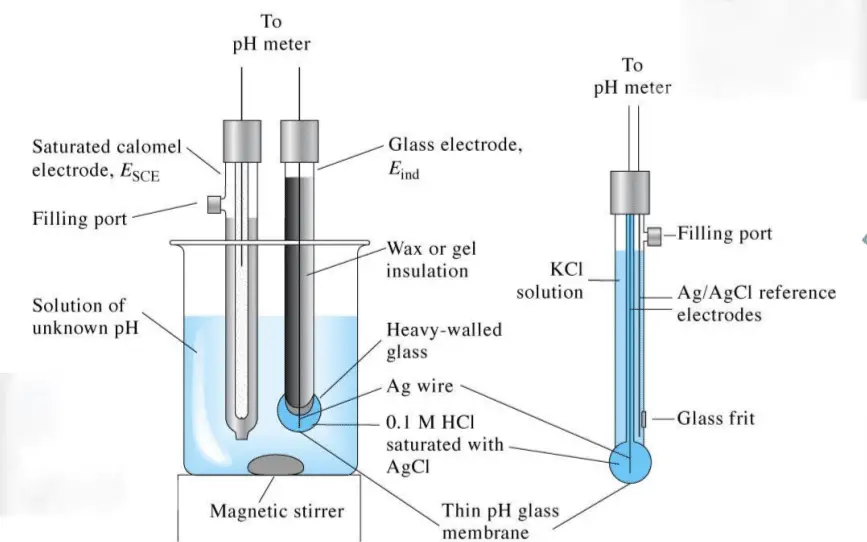
pH Sensor: The pH sensor is the heart of a pH instrument. It is a combination electrode that measures the difference in voltage between a reference electrode and a glass electrode. The glass electrode has a special membrane that responds to changes in pH by generating a voltage signal. The reference electrode provides a stable voltage against which the voltage from the glass electrode is measured. The pH sensor must be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurements.
Temperature probe: The temperature probe is used to ensure any temperature variation is corrected automatically. At the tip of the probe is a sensitive glass bulb that detects the acidity or basicity of the solution and at the other end of the probe is a high-input electronic meter that measures and displays the pH. The probe is fitted with an Arm called Probe Arm.
pH Meter: The pH meter is the device that displays the pH measurement. It has a voltmeter attached to a pH electrode because whatever those electrodes do respond as per pH, so that’s why these are called pH responsive electrodes.
Electrodes: Electrode one is here that is the measuring electrode, and it is a tube made of glass. It consists of thin glass with a glass bulb. It consists of a narrow tube or glass with a glass bulb filled with a potassium chloride chemical with a pH of 7.0. It also consists of a silver block of silver chloride attached to a silver element and generates the voltage. It is used to measure the pH of the unknown solution. Then the second electrode of the pH meter is the reference electrode.
The reference electrode is also a glass tube that consists of a potassium chloride solution. The reference electrode consists of a potassium chloride solution, and it is in contact with the mercury chloride block, which is present at the end of potassium chloride. This reference electrode is used to provide a stable zero-voltage connection and to complete the circuit.
Buffer Solutions: Buffer solutions are used to maintain the pH of a solution at a known value. They are used in the calibration of the pH sensor and also in the measurement of pH. Calibrating the pH meter takes three color-coded standard buffer solutions of pH 7.0, 4.01, and 9.21 for calibration
Electrolyte Solution: The electrolyte solution is used to fill the reference electrode. The reference electrode provides a stable voltage against which the voltage from the glass electrode is measured.
Junction: The junction is the point where the reference electrode and the glass electrode meet. It allows the reference electrode to maintain a stable voltage against which the voltage from the glass electrode is measured. The junction can be a ceramic or a porous material, and it must be cleaned regularly to ensure accurate measurements.
Glass Membrane: The glass membrane is a special membrane on the glass electrode that responds to changes in pH by generating a voltage signal. The glass membrane must be kept clean and free from cracks to ensure accurate measurements.
Also Read: Handling of Laboratory Incident in Pharma
Working of a pH Meter
A pH meter measures the concentration of the hydrogen ions in a solution An acidic solution has far more positively charged hydrogen ions in it than an alkaline solution, so it has greater potential to produce an electric current under certain conditions. It is like a battery that can produce a greater voltage. A pH meter takes advantage of this and works like a typical voltmeter. It consists of a pair of electrodes connected to a meter capable of measuring small voltages. It measures the voltage (electrical potential) produced by the solution whose acidity we are interested in, compares it with the voltage of a known standard solution, and uses the difference in voltage (the potential difference) between them to calculate the difference in pH.
Calibration of pH meter
To calibrate the pH meter, turn on the pH meter and allow adequate time for it to initialize. Remove the electrode from the storage solution gently. Clean the electrode by rinsing it with deionized water under an empty waste beaker and finally, dry it by using soft tissue paper. Do not rub the electrode as it can damage the sensitive membrane around it before taking any sample measurements.
First, Calibrate the pH meter by taking three color-coded standard buffer solutions having pH 7.0, 4.01, and 9.21. The first buffer solution always used for calibration is to be a neutral buffer with a pH of 7.0, because the value of the electrode at 7.0 pH is zero so always zero point calibration is preferred first. The second calibration should be near the expected sample pH, either 4.01 or 9.21. Bases should be measured with buffers with a pH of 9.21, while acidic samples should be measured with a pH of 4.01.
Calibration of pH meter by using standard buffer solution pH 7.0: Place the electrodes in the buffer solution with a pH of 7.0 and set the slop to pH 7.0 value, which is the pH of our buffer solution if, the H+ ion concentration determines the needed pH. suppose the concentration of H+ ions inside the glass membrane electrode and solution of buffer solution present outside the electrode is the same. In that case, the pH equals 7.0. Once the standard with pH 7.0 is calibrated, rinse the electrode with distilled water and dry it by using soft tissue paper.
Calibration of pH meter by using standard buffer solution pH 4.01: In the next step, if the sample’s expected pH is acidic, select the buffer solution of pH 4.01, place the electrodes in the buffer with a pH value of 4.01, and press the calibrate button. Allows the pH reading to stabilize at 4.01. if the concentration of H+ ions inside the glass membrane electrode is lower than the buffer solution present outside the electrode, the pH will be less than 7.0. Once the standard with pH 4.01 is also calibrated, rinse the electrode with distilled water and dry it by using soft tissue paper.
Calibration of pH meter by using standard buffer solution pH 9.21: Place the electrodes in the buffer with a pH value of 9.21 and press the calibrate button. Allows the pH reading to stabilize at 9.21 if required pH 10 buffer solution can be used. The concentration of H+ inside the glass membrane electrode is higher than the buffer solution present outside the electrode.
Testing the Given Solution pH: Place the electrodes in the given sample, and then press the measure button to leave the electrodes in your sample until the Reading has stabilized. This will be the exact pH value of a solution. Take the electrodes out, rinse them with distilled water, and dry them by using soft tissue paper.
Read Also: Dissolution Test Apparatus
Precautions
The pH meter has a flexible arm for easy motion of the electrodes in and out of the solutions. When the pH meter is not in use, the electrode is submerged into 3.0 molar potassium chloride solutions to prevent it from drying or direct contact with the environment for a long time. Drying the glass membrane may permanently damage the electrode.
Do not rub the electrode as it can damage the sensitive membrane around it before taking any sample measurements.
Application of pH Meter
- It is used in the agriculture industry to determine the pH of soil.
- It’s also used to test the quality of municipal drinking water and swimming pools.
- It is used to measure the pH value of solutions in numerous chemical and pharmaceutical businesses.
- The pH meter is also used in the food business, particularly for dairy products such as cheese, curds, and yogurts.
Advantages of pH Meter
- Provide High Accuracy for extended periods.
- Easy to clean.
- Required less space to install.
- Pocket-size pH meter is highly reliable and low-cost.
The disadvantage of the pH meter
- Electrodes need to be cleaned timely to remove deposits. It may cause disturbance in Reading.
- Careful handling glass rods properly to avoid breakage.
Conclusion
A pH meter is an electronic equipment that is used to determine the pH of liquids and semi-solids. The features of this indicator were used to determine the acidity or alkalinity of diverse substances precisely. Because it provides reliable readings, the pH meter is more beneficial than other pH indicators used to determine the pH of a liquid or a semi-solid substance.
FAQs on pH Meter
Ans: pH denotes the potential of hydrogen or the power of hydrogen.
Ans: The pH scale is used to determine how acidic or basic an aqueous solution is. Lower pH values indicate more acidic solutions, whereas higher pH values indicate more basic or alkaline solutions. The pH scale is logarithmic and shows the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution in inverse order. At 25°C, a lower pH indicates a higher concentration of hydrogen ions. A pH less than 7.0 is acidic, and solutions with a pH greater than 7.0 are basic.
Ans: The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion activity is used to calculate pH. formula is pH=- log10(aH+).
Ans: pH indicators are used to measure pH by using the fact that their color changes with pH. Visual comparison of the color of a test solution with a standard color chart provides a means to measure pH accurately to the nearest whole number. More precise measurements are possible if the color is measured spectrophotometrically using a colorimeter. The universal indication is a blend of indicators that produces a continuous color change from around pH 2 to pH 10. Universal indicator paper is comprised of absorbent paper that has had a universal indicator injected into it.
Ans: The design of the pH electrodes is significant; they are road-like structures, commonly built of glass, with a bulb at the bottom carrying the sensor. The reference electrode is insensitive to the pH of the solution. It is made up of a metallic conductor that connects to the display, which is made up of a voltmeter that displays voltage in pH units.
Ans: buffer salts of requisite purity can be obtained from the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Other federal authority’s buffer solutions should be stored in appropriate containers that ensure the stability of the pH through the expiry date and fitted with tight closure.
Ans: Yes, Check here
Ans: pH meter calibration shall be performed by two-point calibration, multiple-point calibration, and multiple-segment calibration.
Ans: as per the United States pharmacopoeia temperature should be 25°C and ±2°C. While as per British pharmacopoeia and European pharmacopoeia, the temperature should be between 20 °C to 25 °C.
Ans: If the test sample’s pH is sensitive to carbon dioxide in the air, use pure water that has recently been boiled and then stored in a container designed to keep carbon dioxide out.
Ans: The only way to determine the pH of a gas is to dissolve it in distilled water and measure the result.
Ans: The air probe can become stuck in the reference system’s electrolyte solution, resulting in inconsistent and unstable readings and possibly making it impossible to obtain a reading to remove air bubbles. Shake the probe vigorously in a downward motion to move the air bubbles to the probe’s top end.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].

Very helpful to subject easy understand words