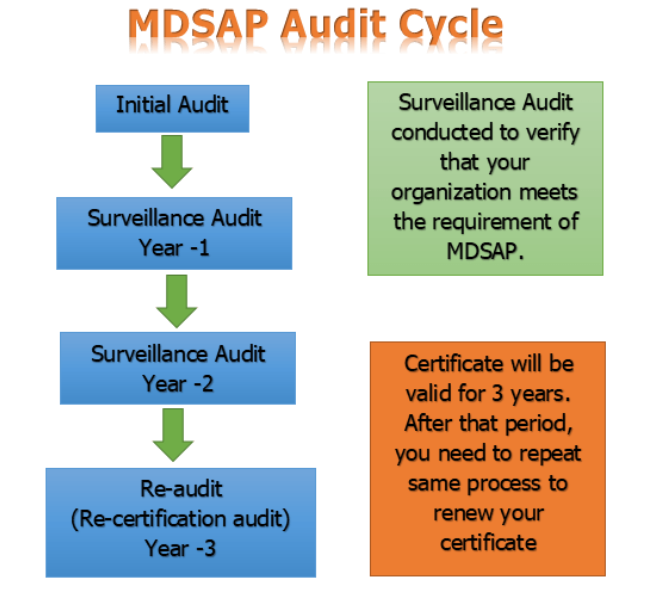
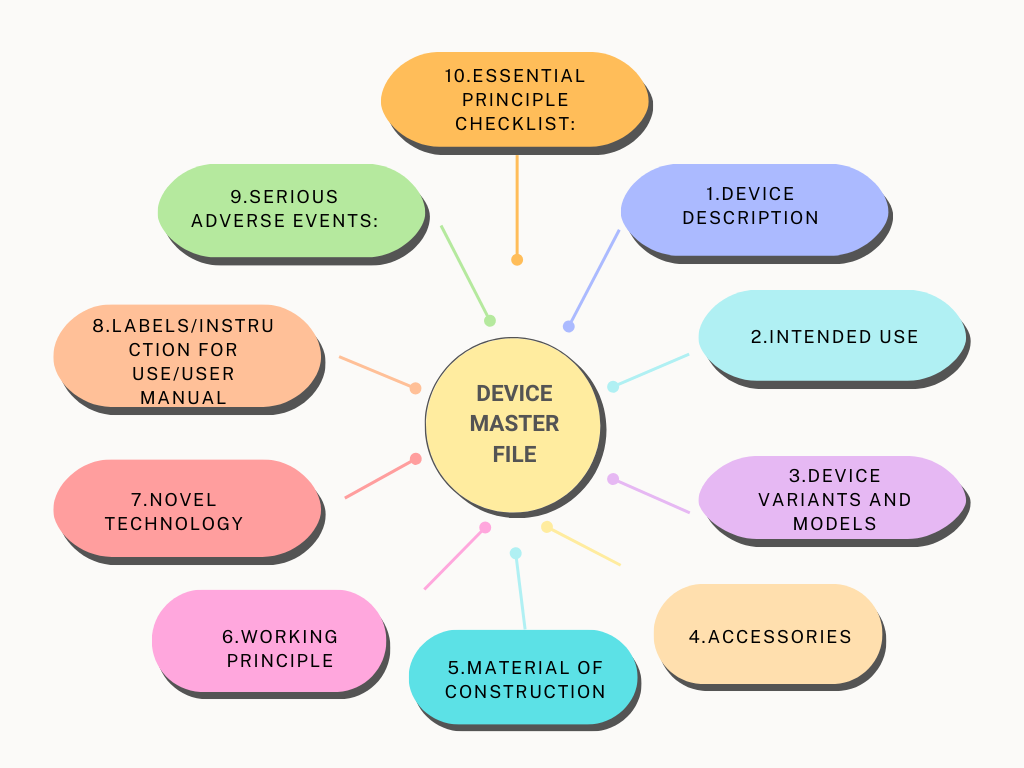
MDSAP Audit: Concepts, Plan and Requirements
Medical Device Single Audit Program, in short form, is termed MDSAP. MDSAP enables the carrying out of one regulatory audit with respect to the quality management system of a medical device manufacturer. MDSAP is a process audit and product approval is still required which is country country-specific procedure. MDSAP has seven chapters and ninety tasks. … Read more