In pharmaceuticals, the solubility of drugs plays a very important role in determining their efficacy and bioavailability. Poor solubility can lead to reduced absorption, irregular blood concentration levels, and inadequate therapeutic outcomes. To overcome these types of problems, scientists and researchers have developed various techniques to enhance Drug Solubility. This article explores the different methods used to improve the solubility of drugs, including physicochemical and physiological Methods.
Facts about Drug Solubility
- In the case of drug absorption, it is important for the drug molecules to reach the site of absorption effectively.
- One of the common reasons for low oral bioavailability is inadequate solubility and permeability.
- These poorly water-soluble drugs show less drug absorption leading to inadequate and variable bioavailability.
- For orally administered drugs solubility is the most important barrier to achieving their desired concentration in systemic circulation for pharmacological response (drug action).
Importance of Solubility in Drug Formulation:
Solubility refers to the ability of a drug to dissolve in a given solvent. When formulating drugs, achieving optimal solubility is essential for several reasons. First and foremost, drugs need to dissolve adequately to be absorbed into the bloodstream and reach their target site of action. Additionally, solubility influences the rate and extent of drug absorption, allowing for consistent therapeutic effects. Therefore, enhancing drug solubility is crucial for improving drug efficacy, bioavailability, and patient compliance.
Challenges in Achieving Drug Solubility
Many drug compounds exhibit poor solubility due to their physicochemical properties. Factors such as high molecular weight, hydrophobicity, and crystal lattice structures can hinder drug dissolution. Poorly soluble drugs often face challenges in oral administration, as they may require large doses or frequent dosing intervals to achieve therapeutic levels. Consequently, researchers have focused on developing techniques to enhance drug solubility and address these formulation hurdles effectively.
Physicochemical Methods for Enhancing Drug Solubility
Particle Size Reduction
One of the most widely used approaches to improve drug solubility is reducing the particle size. Nanosizing or micronization techniques break down drug particles into smaller sizes and the surface area-to-volume ratio increases. The larger surface area allows greater interaction with the solvent, which causes an increase in solubility. This process improves drug wettability and enables faster dissolution rates. Techniques such as milling, high-pressure homogenization, and spray drying are commonly employed to reduce particle size and enhance drug solubility.
Salt Formation
Salt formation involves converting the drug’s acidic or basic functional groups into a salt form. This technique alters the drug’s physicochemical properties, leading to improved solubility. Salt formation exploits the ionization properties of drugs, resulting in the formation of charged species that are more soluble in water.
Solid Dispersion
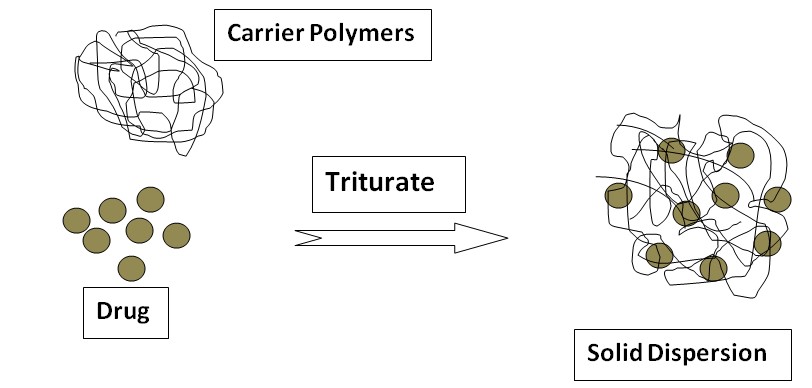
In 1961, Sekiguchi and Obi first introduced solid dispersion to increase the dissolution and oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. It is a dispersion of one or more active ingredients (hydrophobic, water-insoluble drug) in an inert carrier (hydrophilic, water-soluble) at a solid state prepared by the melting (fusion) method, solvent, or melting solvent method. When the solid dispersion comes in contact with the aqueous medium, the inert carrier dissolves and the drug is released ultimately resulting in increased solubility of the drug. Example: Solubility of sulfathiazole increased by the formation of solid dispersion with urea as an inert carrier.
Co-crystallization
Co-crystallization is a technique where the drug molecule forms a crystalline structure with a co-former molecule. The co-crystals exhibit unique crystal lattice arrangements, which can modify the drug’s solubility characteristics. Co-crystallization can increase drug solubility by altering the crystal structure and improving intermolecular interactions. This method offers a versatile approach to enhance drug solubility while maintaining stability.
Co-crystals are special crystalline structures formed by combining two or more components. co-crystals have the ability to enhance important properties of drugs, for example; melting point, solubility, stability, and bioavailability. For instance, when the antitumor drug 6-mercaptopurine is combined with nicotinamide to create cocrystals, the resulting formulation exhibits a dissolution rate that is twice as high as that of the pure drug alone.

Physiological Methods for Enhancing Drug Solubility
pH Adjustment
Adjusting the pH of the drug solution or formulation can significantly impact drug solubility. pH adjustment can be used to convert a poorly water-soluble drug into a more soluble form by exploiting its ionization properties. For example, weakly acidic drugs can be dissolved in alkaline media to increase their solubility. pH adjustment techniques such as buffer systems and pH-modifying excipients are employed to optimize drug solubility in specific physiological conditions.
Complexation
Complexation involves the formation of complexes between drug molecules and complexing agents. Complexing agents, such as cyclodextrins, can form inclusion complexes with drugs, leading to improved solubility. The complexation process enhances drug dissolution by increasing the solute’s aqueous solubility and preventing drug precipitation. In complexation, relatively weak forces such as London dispersion forces, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic interaction are involved.
Micronization
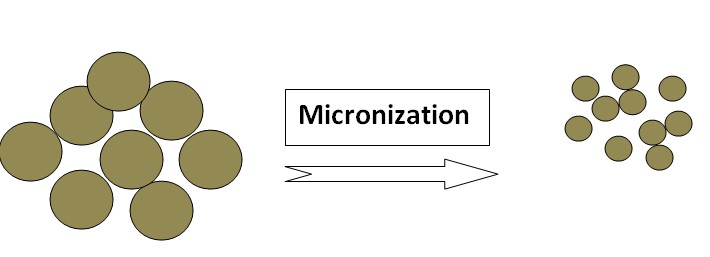
Micronization is a process that reduces the size of drug particles to the micrometer range. This technique improves drug solubility by increasing the surface area available for dissolution. Micronization techniques, including jet milling and high-pressure homogenization, produce finely divided drug particles that dissolve more readily. Micronized drugs exhibit enhanced dissolution rates, leading to improved bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. Examples of drugs whose solubility increased by Micronization: Griseofulvin, Progesterone, Spironolactone & Fenofibrate.
Nanosuspension
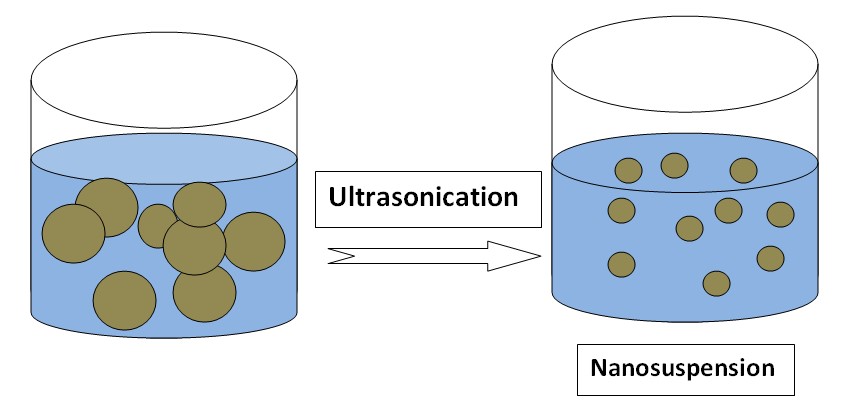
Nanosuspension is a submicron colloidal dispersion of drug particles. A pharmaceutical nanosuspension is defined as very finely colloid, biphasic, dispersed solid drug particles in an aqueous vehicle, a size below 1 um stabilized by surfactants and polymers. Examples of drugs whose solubility is increased by nanosuspension: Carbamazepine, Azithromycin, Ketoprofen.
Use of Solubilizers
Solubilizers are substances that enhance the solubility of drug by forming soluble complexes or micelles with the drug molecules. Solubilizers can solubilize hydrophobic drugs by incorporating them into their hydrophobic cores or by forming stable complexes. Common solubilizers used include surfactants and cosolvents. By incorporating solubilizers into drug formulations, the solubility of poorly soluble drugs can be significantly improved.
Related: Liquid Dosage Form
Table for Differerntaite Physical, chemical, and Other methods
| Physical Methods | Chemical Methods | Miscellaneous Methods |
| pH Adjustment | Particle Size Reduction | Solid Dispersion |
| Micronization | Salt Formation | Supercritical Fluids |
| Nanosuspension | Solid Dispersion | Solvent Change |
| Use of Solubilizers | Co-crystallization | — |
| Complexation | — | — |
Advantages and Limitations of Solubility Enhancement Techniques
Advantages :
The various techniques have several advantages and Limitations in pharmaceutical formulation.
- These techniques can improve drug bioavailability, allow for lower doses, and enable more predictable and consistent therapeutic outcomes.
- Solubility enhancement techniques provide flexibility in drug formulation and can be tailored to specific drug compounds.
Limitations
- Some techniques may require additional processing steps or the use of specialized equipment, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
- The stability of the solubility-enhanced form of the drug must also be carefully evaluated to ensure long-term efficacy and shelf-life.
Conclusion
Enhancing the solubility of drugs is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical formulation. Various physicochemical and physiological methods can be employed to improve drug solubility, including particle size reduction, salt formation, solid dispersion, co-crystallization, pH adjustment, complexation, micronization, and the use of solubilizers.
Reference: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0974694313001473
FAQs on Drug Solubility
Drug solubility is the ability of the materials of the drug product to completely dissolve in a solvent like; water. It is a critical property that affects drug absorption, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy.
Drug solubility is directly related to the drug absorption rate, which directly affects the bioavailability of a drug. Poor solubility can lead to reduced bioavailability and inadequate therapeutic outcomes.
Several challenges contribute to the poor solubility of Drugs, including high molecular weight, hydrophobicity, and crystal lattice structures. These factors can impede drug dissolution and hinder absorption.
Particle size reduction increases the surface area of the drug, allowing for faster dissolution and improved solubility. Smaller particles have a larger interfacial area, enhancing their interaction with the solvent.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
