Paddles mixture act as impellers which are used in the process of blending liquids. They have flat blades attached to a vertical shaft, rotating at a speed below 100 r.p.m. In this article learn about the Paddles mixture and their Principle, Construction, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications.
Principle behind Paddles
It works on the principle of Shearing force. Paddle agitators operate by generating a consistent laminar flow of liquids. The paddles exert radial and tangential force on the liquid, with minimal axial movement unless the blades are pitched.
Related: Silverson Mixer
Construction of Paddles
A paddle consists of a central hub with vertically attached, elongated flat blades. Paddles may be of two or four blades, as described in the figure below. The blades may be pitched, containing a dish or hemispherical shape with a large surface area compared to the tank where they are used. Paddles rotate at a low speed of 100 r.p.m. In deep tanks, multiple paddles are mounted on the same shaft, stacked one above the other.
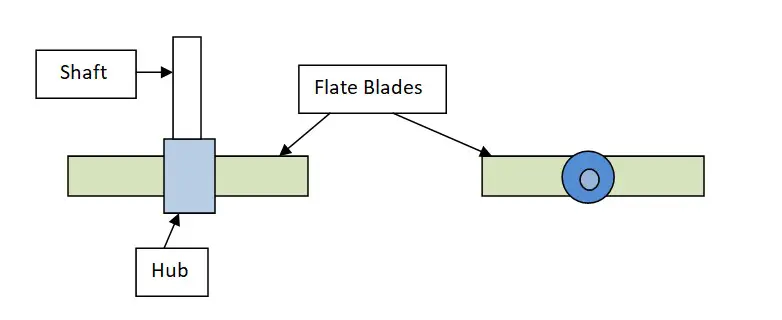
Working of Paddles
The material to be mixed is introduced from the top of the trough. The shaft blades carrying hab blades rotate at a low speed of 100 RPM. They push the liquid Radialy and tangentially. The normal filling level is slightly above the shafts, allowing for creating more space in the mixer trough to enable the free movement of particles. The random motion within the trough yields a mixing homogeneity of approximately 98-99%.
Related: Turbine Mixture
Advantages
- The use of paddle impellers minimizes the vortex formation due to their low-speed mixing.
- These mixers are suitable for slow operations, characterized as heavy-duty.
- They effectively blend systems utilizing 2 or 4 blades.
Disadvantages
- Mixing suspensions is not their strong suit, so it may require the use of baffled tanks.
- Their heavy-duty work results in high power consumption.
- They lack efficiency in blending a variety of materials with varying consistencies.
Applications of Paddles
- Paddles applications include the production of antacids, suspensions, and antidiarrheal mixtures, such as bismuth-kaolin mixture.
- They are used in the mixing of solids, slurries, and crystals during the super-saturated cooling phase formation.
Price
The pricing of paddle mixers can vary depending on factors such as size, specifications, and manufacturer. It is recommended to contact specific suppliers or manufacturers for accurate pricing information.
Conclusion
Paddles play a vital role in the mixing and blending of liquids. It has various advantages such as low-speed operation, reduced vortex formation, and the ability to handle heavy-materials. However, they have limitations, if talk about mixing of suspensions and blending materials with different consistencies.
FAQs
Ans: Yes, paddle mixers are capable of effectively blending of viscous liquids and semi-solids due to their large blade surface area.
Ans: Baffles are generally required for high-speed paddle mixer operations to improve the mixing efficiency, particularly in case of suspensions.
Ans: Paddle mixers rotate at speeds below 100 r.p.m.

