Fluid energy mill: A fluid energy mill is used for size reduction in the pharmaceuticals, cosmetics,s and food industries. the fluid mill works on impaction and attrition.
Principle:
Fluid mills operate on the principle of impact and attrition.
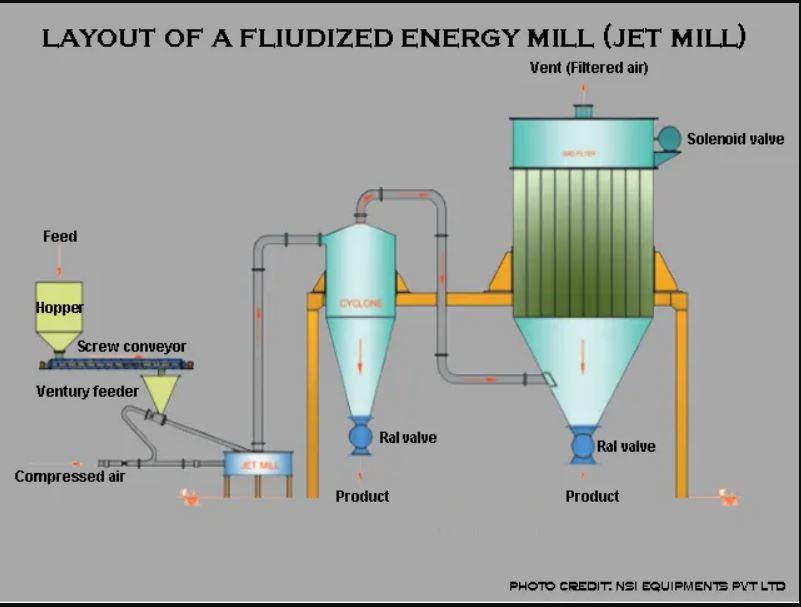
Working of fluid energy mill:
Start the fluid energy mill and pass the feed through the inlets of the venturi. the air entering through the grinding nozzle transport the power in the elliptical or circular truck of the mill. the high-velocity air stream passed and the milling takes place because of the high-velocity collision between the suspended particles.
Suspended particle colloids with each other and break. thus impact and attrition forces required to achieve size reduction. the result in small particles is carried out through outlets or removed by the filters.
The coarser particle undergoes re-circulation in the chamber and again colloids with the new feed materials.
Construction of fluid energy mill:
It is connected by an elliptical pipe that has a height of 20 to 200 mm. made up of pharma-grade stainless still and tough ceramics.
The fluid mill is connected with a grinding nozzle usually (2 to 6)with a diameter that may be placed tangentially and opposite to the initial flow path of powers, a compressed air passes with 600 kilopascals to 1 megapascal.
Inert gases can be used to minimize or eliminate the oxidation of susceptible compounds.
A Venturi feeder is provided in the path of airflow. an outlet with classified is fitted to allow the escape of air.
It connects with the outlet with a classifier it allowing the escape of the air.
Read Also: Ball Mill; Principle, Working, and Construction
Pharmaceuticals usages of fluid energy mill:
- It is used where the product is highly heated and sensitive like antibiotics and vitamins.
- Preferred when strict quality control is desirable
- To get the ultra-fine grinding
- It generally proceeds with moderately hard materials.
- It can reduce the particle to 1 to 20 microns
Advantages:
- It has no moving parts
- No heat generation (so it is highly required for thermolabile substances like sulphonamide, vitamins, and antibiotics)
- No chance of contamination
- The expansion of gases under pressure produces cooling effects.
Disadvantage:
- Not suitable for soft, Tucky, and fibrous materials
- It is expensive equipment
- Not easy to clean

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
