Medical Device Single Audit Program, in short form, is termed MDSAP. MDSAP enables the carrying out of one regulatory audit with respect to the quality management system of a medical device manufacturer. MDSAP is a process audit and product approval is still required which is country country-specific procedure. MDSAP has seven chapters and ninety tasks. Members include Australia, Brazil, Canada, Japan, and United States CDC among others. MDSAP is quite similar to ISO 13485:2016 and has additional country-specific requirements. The audit cycle is same as ISO 13485:2016.
HISTORY:
The foundational work was created by GHTF (Global Harmonization Task Force) and it was taken up by IMDRF (International Medical Device Regulatory Forum) in 2011. A pilot program was launched in January 2014 for three years and replaced by a full program in January 2017.
Related Topic: Documents Required for Class A Medical Device
MDSAP Audit Cycle:
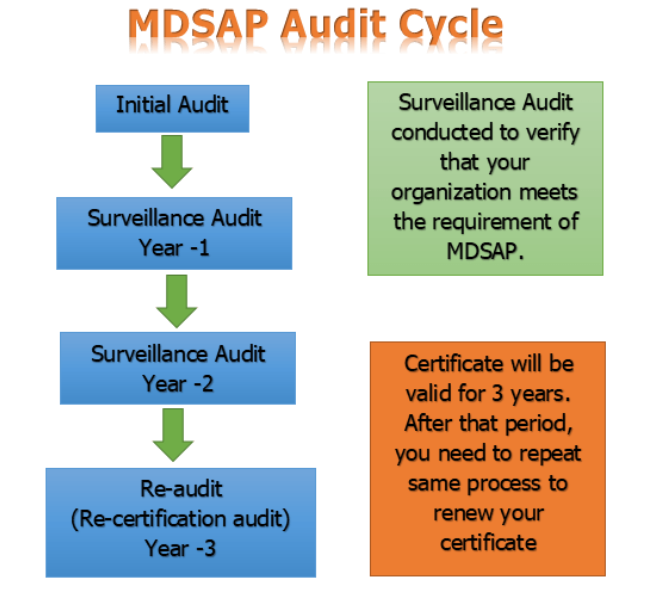
Types of MDSAP Audit:
There are two types of audits applicable in some circumstances:
Unannounced Audits:
MDSAP participating authorities require certification bodies to conduct unannounced audits in circumstances where high-grade non-conformities have been detected.
Special Audits:
These are extraordinary audits that are not part of the planned audit cycle. These types of audits should only be performed if necessary and on selected aspects of the medical device organization’s quality management system. For example: Extension in the scope of existing certification, following critical findings of MDSAP audits.
Purpose of MDSAP:
To Lower the Cost of audits as compared with the conducting of an independent audit. No additional requirements for manufacturers. A single audit adjusts the time.
Process Flow Chart for MDSAP Certification:
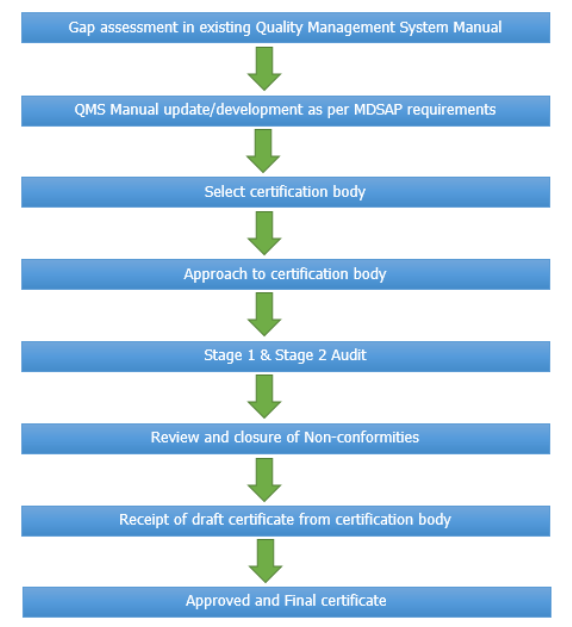
Chapter and task details:
Chapter 1: Management = Tasks: 11 Nos.
Chapter 2: Device marketing authorization and Facility registration = Tasks: 3 Nos.
Chapter 3: Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement = Tasks: 16 Nos.
Chapter 4: Medical Devices Adverse Events and Advisory Notices = Tasks: 2 Nos.
Chapter 5: Design and Development = Tasks: 17 Nos.
Chapter 6: Production & Service Control = Tasks: 29 Nos.
Chapter 7: Purchasing = Tasks: 12 Nos.
MDSAP Members:
- Therapeutic Goods Administration of Australia
- Brazil’s Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária
- Health Canada
- Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
