Transdermal patches are used on the skin to deliver medicines directly into the bloodstream. In this article, read about transdermal patches, their working mechanism, advantages, applications, types, application methods, and safety considerations.
What are Transdermal Patches?
They are thin, adhesive patches that are applied directly on the skin to deliver medication. Transdermal patches are useful over oral medications because they require digestion or injections that may cause discomfort. They also provide a non-invasive and controlled delivery system. The patches are designed to release medication gradually over an extended period. It ensures to deliver a constant rate of the drug in the body.
How Do Transdermal Patches Work?
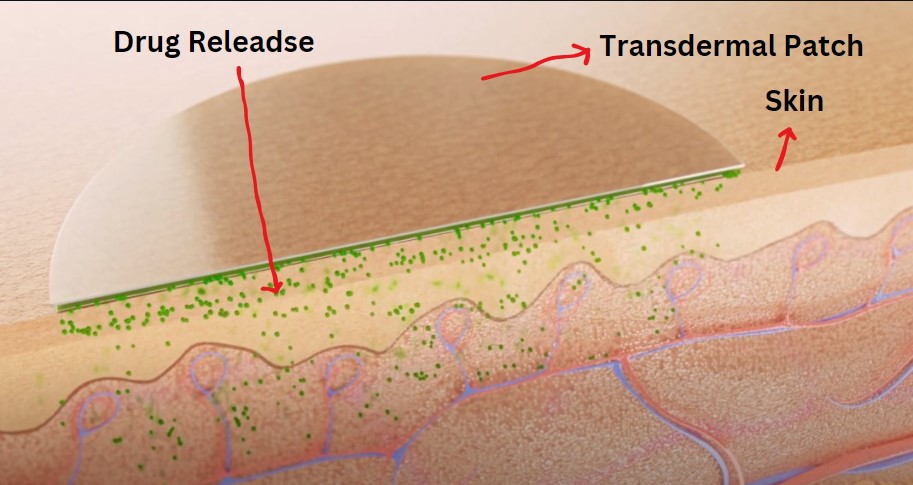
The patches consist of three layers i.e. drug reservoir, adhesive, and backing. The adhesive layer ensures that the patch adheres to the skin. The drug reservoir contains the medication, which is released through the skin into the bloodstream. The backing layer protects the patch and prevents drug loss.
Advantages of Transdermal Patches
Transdermal patches have the following advantages:
- They provide a controlled release of medication, maintaining consistent blood levels, and avoiding sudden peaks and troughs.
- Controlled delivery over days, anywhere from 3 to 7 days, and minimizes side effects and enhances patient compliance.
- They eliminate the need for frequent dosing, reducing the chances of missed doses.
- They also bypass the digestive system, which can be advantageous for individuals with sensitive stomachs or gastrointestinal issues.
- An alternative for individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills.
- It can avoid drug metabolism through the liver
Applications of Transdermal Patches
They are commonly used for pain management, hormone replacement therapy, smoking cessation, motion sickness prevention, and the treatment of conditions like hypertension, angina, and Parkinson’s disease.
In the cosmetic industry, these patches are used as anti-aging or skin-rejuvenating ingredients.
Types of Transdermal Patches
There are different types of transdermal patches as below:
Matrix patches: Matrix patches contain the drug dispersed uniformly within the adhesive layer.
Reservoir patches: Reservoir patches have a separate drug reservoir that releases medication through a membrane.
Vapor patches: Vapor patches use volatile substances that evaporate upon application, delivering the drug through the skin.
Related: Techniques used to Enhance Drug Solubility
Choosing the Right Transdermal Patch
The factor that is required to keep in mind while choosing the Right Transdermal patch is there drug’s properties, dosage requirements, duration of treatment, and patient-specific considerations.
How to Apply Transdermal Patches
Stepwise procedures for applying these Patches are as Follow:
- The skin should be dry, clean, and Hair free
- Appling on the affected area i.e. back, chest (not over the heart), side of the waist, or upper arms.
- Read all the applying instructions provided on patches.
- Apply it by slightly pressing on the skin, and ensure proper adhesion.
Precaution: To prevent any skin irritation, rotate the site or apply near the previous area.
Potential Side Effects
While transdermal patches are the safest method. But sometimes it may cause side effects like; skin irritation, redness, or itching the skin. In some cases, the patient may feel an allergic reaction. So it is recommended to meet with your doctor/Pharmacist before applying itself on the skin.
Precautions and Safety Considerations
Following Precautions and Safety Considerations shall be kept in mind before it uses:
- Avoid applying patches to broken, damaged, or irritated skin.
- inform a doctor about any allergies, medical conditions, or medications.
- Store patches properly, as per the storage instruction on the label.
Transdermal Patches vs. Other Delivery Methods
Transdermal patches have lots of advantages compared to other drug delivery methods. If you take oral medications that undergo digestion and may be affected by stomach acid, But in the case of transdermal patches, They bypass the gastrointestinal system, hence overall it improved drug bioavailability. Patches also help in the controlled release of drugs in the body, eliminating the need for frequent dosing or injections. They also help in reducing pain and discomfort for patients.
Related: Depilatory | Hair Removal Methods
Conclusion
Transdermal patches are widely manufactured and recommended to patients because of their advantages like; high bioavailability and controlled release of drugs for a longer time. It is also useful for the patient who has gastrointestinal problems. So today it is a very effective method to deliver drugs to the body without any higher risk.
FAQs
Ans: Thet are suitable for many patients, But it is recommended to consult a doctor or pharmacist before use.
Ans: Cutting or trimming transdermal patches can lead to loss of drugs, hence it can affect drug dosing requirements so It is best to use patches as directed in the product label.
Ans: Yes, in the case of water-resistant patches. It is best to read labels before going swimming.
Ans: The onset time for patches is fast because it is directly absorbed into the bloodstream via skin.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
