Aerosol (Aerosols) is a self-Pressurized packaging form, consisting of a metal, glass, or plastic container with a permanently attached continuous or metering valve, and designed to dispense products as sprays, streams, gels, foams, lotions, or gases. Approximately 90% of aerosol cans are tinplated steel and 10% aluminum. Aerosol is a suspension of line solid particles or liquid droplets in a pressurized gas. Suspension aerosols delivering the drug into the respiratory tract must have a particle size in the range of 1-5 micro and no particle should be large than 10 micrometers. A dispensing device that produces an aerosol mist of liquid particles is known as an aerosol spray.

Working of Aerosol
This is used with a can or bottle that contains a liquid under pressure. The liquid is driven out of a small hole and emerges as an aerosol or mist when the container’s valve is opened. As the gas expands to drive out the payload, some propellant evaporates inside the can to maintain an even pressure. Outside the can, the droplets of propellant evaporate rapidly, leaving the payload suspended as very fine particles or droplets. Typical liquids dispensed in this way are insecticides, deodorants, and paints. An atomizer is a similar device that is pressurized by a hand-operated pump rather than by stored gas.
Usually, the gas is the vapor of a liquid with a boiling point slightly lower than room temperature. This means that inside the pressurized can, the vapor can exist in equilibrium with its bulk liquid at a pressure that is higher than atmospheric pressure (and able to expel the payload), but not dangerously high. The escaping gas is quickly replaced by evaporating liquid. Because the propellant is liquid in the can, it should be miscible with the payload or dissolved in it.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) an organic compound that contains carbon, chlorine, and fluorine have been replaced in nearly every country due to the negative effects CFCs have on Earth’s ozone layer. The most popular substitutes are volatile hydrocarbon mixtures, such as propane, n-butane, and isobutane. Dimethyl ether (DME) and methyl ethyl ether are also used. All these have the disadvantage of being flammable.
Food is also delivered using nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide as propellants (for example, whipped cream and cooking spray). Medicinal aerosols such as asthma inhalers use hydrofluoroalkanes (HFA): either HFA 134a (1, I,1,2,-tetrafluoromethane) or HFA 227 (1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane) or combinations of the two.
Components of Aerosols Container
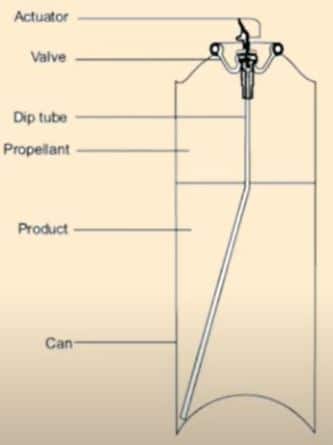
a. Propellants: Pro[ellant is either liquefied gas or compressed gas,
b. Containers: Generally tinplated steel and aluminum
c. Dip tube: Polyethane and polypropylenerrha 19
d. Valve and actuator: Valve contains ferrule or mounting cap, valve body, dip tube, and metering valves.
• Ferrule joins the valve properly to a container.
• Valve body has an opening for attachment of dip tube. It contains a vapor tab which will produce fine particles size, prevent clogging of the valve
Types of Aerosol systems:
Two-phase system: Propellent or its mixture + active ingredients which are soluble in solvent which is soluble propellant or directly in propellant constitutes 1st phase and 2nd phase is vapor phase or vapors of propellents.
Generally, 5% propellant for foams, and 95% propellant for inhalations pdts are used.
To prevent the settling dispensing Particles in suspension oleic acid is used as a suspending agent to prevent agglomeration because it can cause clogging of the valve and result in an error in dose administration.
Three-phase system: for topical in which active ingredients are not soluble in propellants so another solvent is used Constitutes Ist phase, this solution is immiscible with liquid propellants (2nd phase) and 3rd phase is vapor phase. Water-based aerosols involve three-phase stems.
Foam dispensing aerosols: uses CO2 and N2O.
Manufacturing of aerosols:
Cold filling: low-temperature range -34 to 40 “C. But it is not suitable for aqueous pills and temperate sensitive preparations.
Pressure filling: used for all types of aerosols.
Quality control test for pharmaceutical aerosols:
- Flame projection test and Flashpoint test (using Stel Tagopen Cup apparatus): for flammability and combustibility
- Particle size determination: By using Cascade, Impactor, and Light scattering decay)
- Identification of propellants: By gas chromatography and RI
- Foam stability: visual evaluations and time for a MASS to penetrate the foam rotational viscometer.
- Dosage with metered valve: from reproducibility of dosage each time the valve is suppressed.
- Vapor pressure is measured by the pressure gauge
- Density: measured by pycnometer or hydrometer.
- Moisture content; measured by the Karl-fisher method
- Performance; valve discharge rate
Advantages of Aerosol:
- Reduce chances of contamination from the materials because of direct use in affected areas.
- The amount of drugs can be delivered directly to affected organs in the desired form.
- Easy to use without any mixing of external components.
- Aerosol administration provides immediate and effective relief.
Because the medicine is not exposed to ambient oxygen and moisture while stored in MDIs and DPIs, its stability is improved. - Aerosol medication administration is a quick process.
- It protects the medication against breakdown in the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is possible to escape hepatic first-pass metabolism.
- Aerosols can be used for systemic and local purposes.
Related Searches: Gels in Pharmaceuticals
The disadvantage of Aerosol:
- The dose form is costly.
- Difficulty in discarding empty containers
- Allergic reactions in some cases
- it may cause an explosion
- Aerosol dosage forms of insoluble drugs are challenging to manufacture.
- Propellants can sometimes create a harmful reaction.
- Sometimes it contaminates pharmaceuticals due to the presence of trace metals in the container.
FAQs
Aerosols
Cascade impactor and Light scatter decay
Trichloromonofluoromethane
Polypropylene
Metered valve
Gas Chromatography and IR Spectrophotometer
Epinephrine
Trichloromonofluoromethane

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
