Sometimes we may confused when it comes to understanding the difference between moisture content and Loss on Drying (LOD). To clear your doubts, please read the entire section of this post. Firstly, let’s discuss about moisture analyzers. A moisture analyzer is used to determine the water content in a sample. Then a few questions arise about it: How many types of moisture analyzers are used in the pharma industry to determine LOD? What is the principle of a moisture analyzer? How to calculate moisture content and LOD? Let’s discuss them one by one.
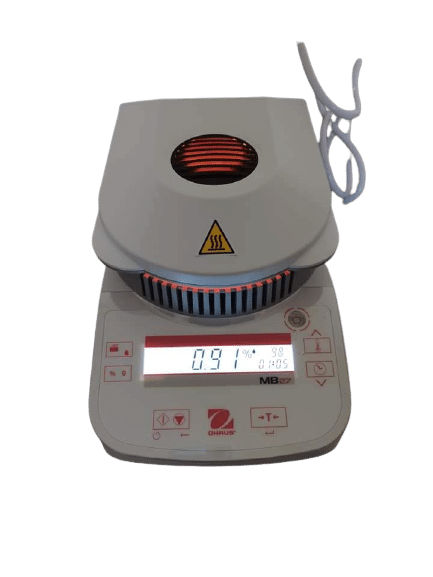

Types of Moisture Analyzers
- IR moisture analyzer
- Halogen Moisture analyzer
- Gravimetric moisture analyzer (Not Much needed)
IR analyzer: The IR moisture analyzer is the equipment used to determine the moisture content of a sample using the loss on drying method. It consists of a weighing unit to measure the sample weight and a heating unit that uses IR (infrared) to heat the sample.
Halogen analyzer: A halogen analyzer emits Infrared radiation and radiates moisture that is present in the sample.
What is Moisture content?
Moisture content is the amount of water present in the sample.
Formula for % moisture content:
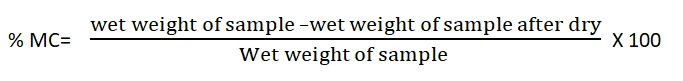
Principle of Moisture Analyzer:
The principle of moisture analyzer works on the thermos gravimetric method, which is also referred to as the “loss on drying” principle.
Loss on Drying (LOD) test:
The loss on drying test is designed to measure the amount of water and volatile substances present in a sample, expressed as w/w (weight by weight) when the sample is dried under specific conditions.
The formula for % LOD check:
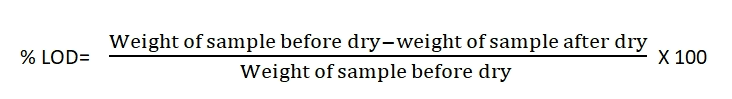
Difference between moisture content and (LOD):
The Karl Fischer titration method is used to determine the moisture content in a sample, and the result only contains water. This means that the result does not include any other volatile content present in the sample.
To measure the drying loss, including all volatile materials (including water content and solvents), the sample is heated below its melting point in an oven at specific conditions (usually 105°C for 3 hours).
Read Also: pH Meter | Principle, Calibration, and Working

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
