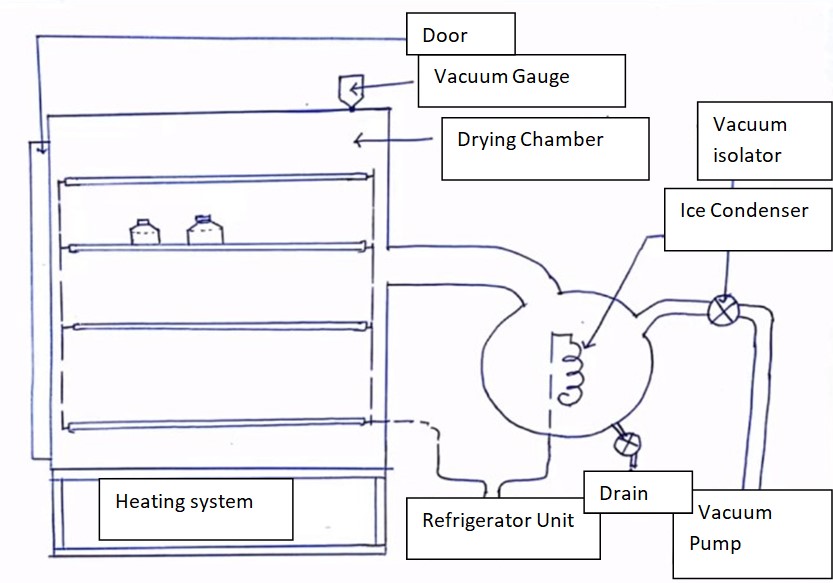
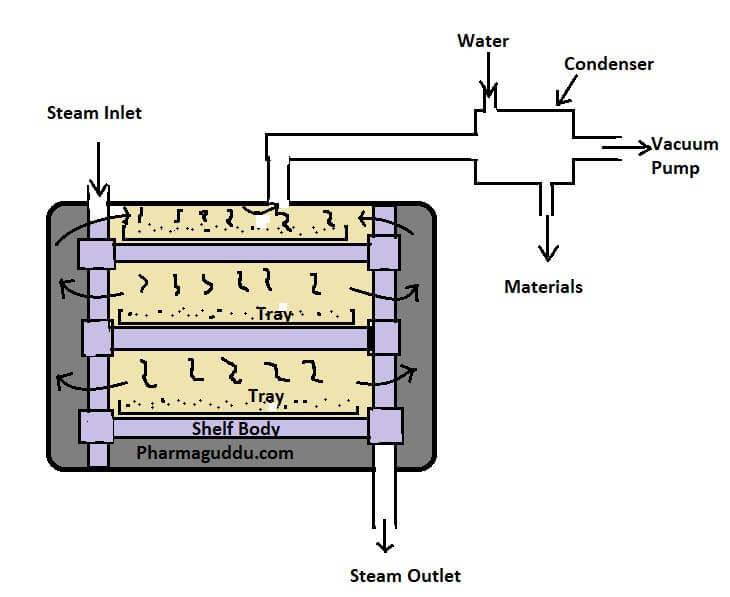
0.1 M Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), Preparation and Standardization
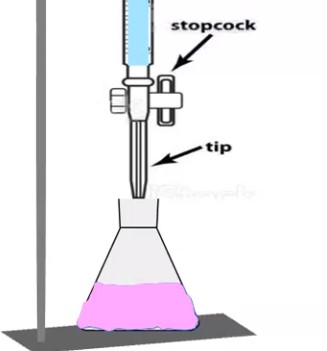
Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 M Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) in the Laboratory. Reagents: 1 Sodium hydroxide 2 Potassium hydrogen phthalate 3 Phenolphthalein solution. Chemical Reaction Principle: In this process, we will directly measure the strength of potassium hydrogen phthalate by using sodium hydroxide. To find the endpoint, we’ll use phenolphthalein as an indicator. Let’s understand … Read more