Handling Scrap And Disposal coming from any regular production run assumes great significance in the pharmaceutical industry. Improper destruction procedures followed can lead to a problematic situation if such material finds its way into the wrong hands.

1) Objective: To lay down instructions for the management of Scrap generated in different departments of the Organisation to ensure correct handling & disposal.
2) Scope: It provides an overview of the generation of reject/scrap, its collection, and accounting, and recommends guidelines for dealing with the rejects/scrap and its disposal thereof.
3) Responsibility: The responsibility for dealing with rejects/ scrap rests on the representatives of Quality Assurance and the store’s department for its final disposal in such a manner that it cannot be misused.
a) Officer and Housekeeping Person-Correct Handling Scrap And Disposal of Scrap in the department, transfer Scrap to the scrap yard.
b) Q.A. Officer-Periodic inspection of Scrap in the scrap yard.
c) Manager Stores- Final disposal of Scrap.
4) Receipt of Scrap/Reject :
a) Receive the Scrap generated by the concerned production department.
b) Place specified Scrap in a designated area of the scrap yard.
c) Inform the concerned department in charge in case of any discrepancy.
d) Ensure that there is no spillage of scrap/reject on the floor during transfer.
5) Reject/Scrap Generation :
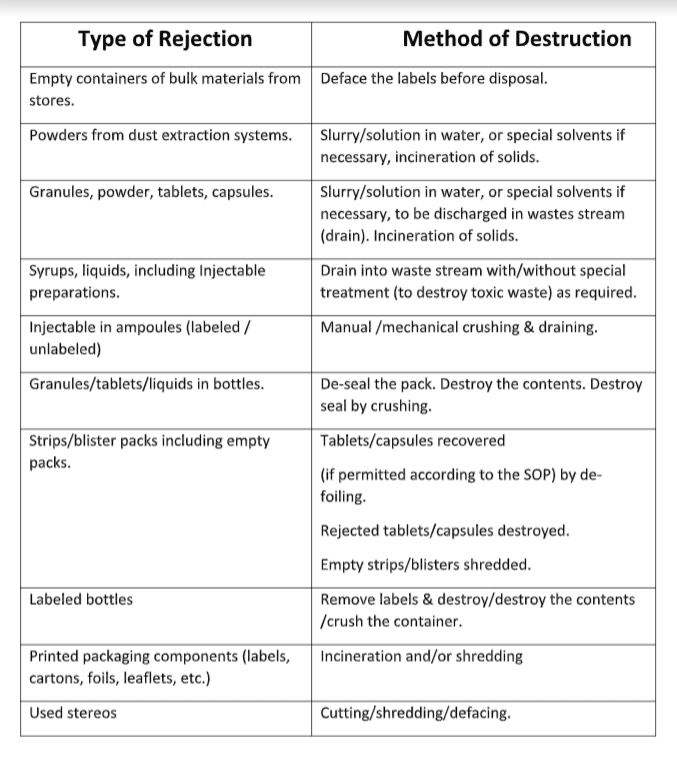
Rejects generated at various stages of pharmaceutical product manufacturing sites must be systematically collected, accounted for, and disposed of correctly to prevent misuse.
a) Product rejects from material processing and transfer operations must destroyed on the shop floor.
b) Product residues extracted into dust extraction system at various stages of manufacture or leftover in various processing equipment and machinery destroyed on the shop floor.
c) Rejects generated during compression, encapsulation, coating, filling, and inspection stages must destroyed on the shop floor.
d) Rejects resulting from in-process checks, such as weight variation, volume checks, and strip leak testing, must be destroyed on the shop floor, while packing materials are to be sent to the scrapyard.
e) Excess or rejected printed packing materials like labels, leaflets, foils, and tubes must be defaced/shredded at the end of the packing operation and sent to the scrapyard.
f) Excess or used stereos after completion of batch coding to be destroyed by doing small pieces.
g) Obsolete printed packing materials in the stores shall be defaced /shredded in a scrapyard.
h) Excess samples that remain after the testing, shall be destroyed in the laboratory.
i) Control samples in the custody of IPQA after the mandatory storage period shall be destroyed in the laboratory.
6) General Principles :
a) There shall be written authorized procedures for :
i) Determining recoverable residues from non-recoverable rejects.
ii) Scrap that is disposed of commercially as solid waste requires the person to take precautions, such as defacing labels on empty bulk containers, corrugated Boxes, cartons (unprinted), and more.
b) There shall be a written, authorized procedure for handling the destruction and disposal of rejects generated during the production/handling of pharmaceutical products and printed packing components.
c) All reject items should go into proper closed containers, be labeled correctly, and be kept in a secure segregated area until they get taken for disposal.
d) Destruction must be carried out by authorized persons under the supervision of a responsible person.
e) Quantities rejected and destroyed must be recorded and reconciled in the relevant batch documents as per the “reconciliation and destruction of materials” SOP.
f) Rejected printed packing materials shall not be returned to suppliers.
g) Appropriate safety precautions must be taken while carrying out destruction.
h) Final disposal of residual solids/liquids shall be consistent with local regulatory requirements, including its effect on the environment.
Related: Handling of Disposal in Tablets
7) Inspection of Processed Scrap By Quality Assurance before Final disposal:
a) Processed Scrap should be kept in the scrap yard for periodic Q.A. inspection.
b) Ensure that shredding/destroys the identity of all printed/overprinted materials by cutting them into small pieces.
c) Check and ensure that the labels on all the containers are correctly defaced.
d) Checked and ensured that all the containers of Injectables/drops were crushed.
e) After complying with all the above checks, clear the Scrap for final disposal after noting all entries.
8) Final Disposal of Scrap from Scrap holding area to scrap yard:
a) After obtaining the Q.A. clearance, properly close the containers /poly bags holding the Scrap on a pallet in the designated area.
b) Place the Scrap separately based on the following classification:
- Glass scrap
- Plastic Scrap
- Paper scrap
- Blister /strip scrap
c) Lock the scrapyard after keeping the Scrap inside.
9) Disposal of Scrap from Scrap Yard:
a) Weigh each container of the Scrap and enter the item’s details and the weight in the register maintained for the purpose.
b) Load each item into the vehicle. Ensure that the details are checked and countersigned by a security officer and the representative of the scrap contractor.
c) Prepare gate pass mentioning all the items being dispatched.
d) Counter-check the details in the gate pass with the scrap yard register. If found correct, allow the vehicle to pass.
10) Abbreviations:
IPQA-in-Process Quality Assurance
QA- Quality Assurance
SOP- Standard Operating Procedure

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
