
Data integrity is a key approach in the pharmaceutical quality control system. ALCOA stands for (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate). It was introduced in the 1990s to ensure the framework for data integrity and good documentation practice (GDP). Then further introduced another term called ALCOA+. ALCO+ stands for (Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available) currently used by the FDA, WHO, PIC/S, and GAMP. So over periods, data integrity concepts expand from ALCOA to ALCOA plus for ensuring data security and integrity ( data protection).
ALCOA and ALCOA plus are related to data, either on paper or electronic form, and defined by FDA guidance.
9 Principles of ALCOA and ALCOA+ with Examples:
ALCOA has five basic principles (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate) to stop data integrity issues.
Attributable: The collected data must be attributed, who performs the action and when, if a record is changed, who did it and why?

Attributable example, when conducting validation, the test results must be dated, and the initial validation should be done by the person involved in conducting the test. If there is any change in the monitoring system, the details of the change should be in the audit trail, and any corrections made by the person should be recorded and dated. A signature log must be maintained for the identification of initials and the person who completed the paper record.
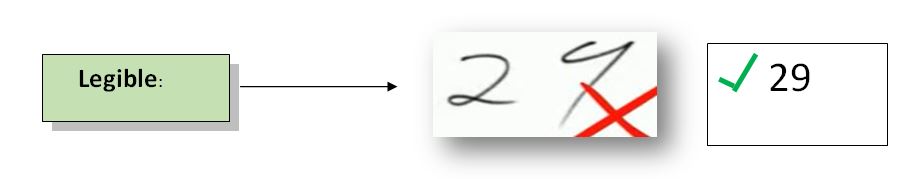
Legible: Data must be recorded permanently in a durable record medium and easy to read. If data records are permanent and readable, they can be easily assessed through the entire product data lifecycle. It helps in the easy retrieval of all previous data if needed.
Contemporaneous: The data should be recorded at the time and date of work performed. The timestamp should we follow in order.
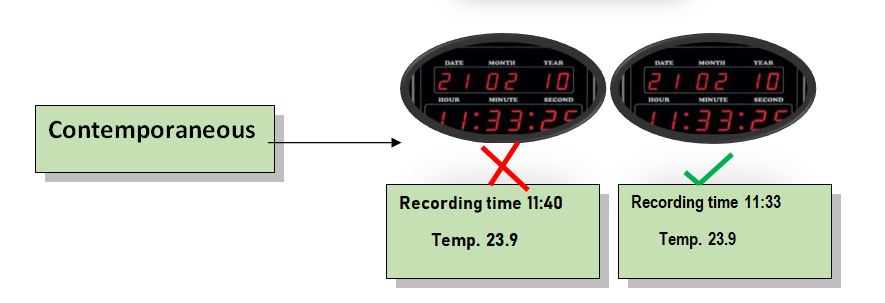
Contemporaneous For example, when conducting validation protocol, the result of the test performed should be recorded in an online sequence. Recording the results should be dated with a timestamp and then logged into the electronic system.
Original: The information must be recorded as original or in a certified true or original copy; this may be an acceptable protocol, a database, or a notebook.
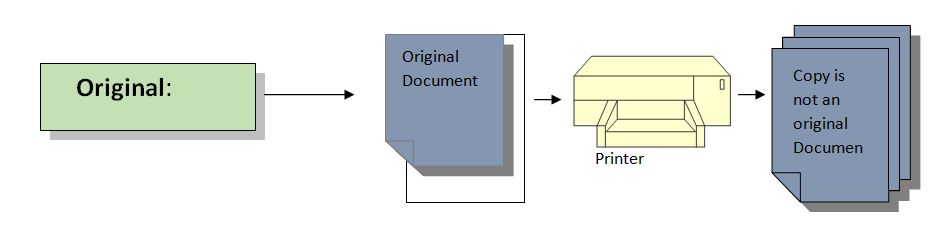
For example validation test is being recorded on a given protocol because recording test results in a Notebook may be a chance of error. If the original data is handwritten, it must be stored in an electronic system.
Accurate: No error or editing was performed without documented amendments to ensure the accuracy of the data and records. The data must have the following characteristics.
- It should be complete
- It should be free from error
- It should be e reflective of the observation
Any change made to the recorded data should be documented to ensure the accuracy of the data collected. Follow security checkups in the electronic system. Ensure there is a witness to check for any critical data collection.
ALCOA PLUS (+)
Complete: All data should be complete including, test repeat or re-analysis performed on the sample.
Consistent: Being Consistent in the generation of records and application of date and time stamps in the expected sequence.
Enduring: Data should be recorded in a controlled worksheet in laboratory notebooks or invalidated Electronic systems.
Available: Data need to be available and accessible for audit review and inspection over the lifetime of the record.
What is Data integrity?
Data integrity is the key element in pharmaceuticals to ensure products meet all the quality standard parameters up to the end of products. It is the process of maintaining and assuring the promise and consistency of data over its whole life cycle.
What is the common Data integrity issue?
Two types of common Data integrity issues are as follows:
- Intentional issue
- Non-intentional issue
- Intentional issue: To maintain the regulatory standard, faculty must have cGMP and a defined procedure. The person working in an organization who knowingly does not follow the cGMP and defined procedure and hides wrong things is committing crimes intentionally. Such type of activity causes a huge impact on the organization, such as form 483 and a warning letter In such cases facility or organization to terminate the person who is doing wrong with data. Intentional data integrity issues are a violation of cGMP and regulatory compliance. Non-compliance such as manipulation alteration, falsification, deletion, and modification of the data to get the final result at an acceptable level is not allowed in the pharmaceutical industry
- Non-intentional issue: The non-intentional issue may happen when a lack of knowledge, training, and experience in such cases an organization can conduct root cause analysis on Data integrity issues if found guilty organization must provide proper training to the person to avoid Data integrity issues.
Why is Data integrity important at that moment?
If any Data integrity issues are found, regulatory bodies take action because of violations. Action may be includes warning letters and holding of import. The recently large number of warning letters issued by regulatory is related to Data integrity issues.
The international regulatory authority is more concerned about Data integrity issues. So the FDA decided to give training to regulatory Agencies like MHRA to better recognize Data integrity issues.
In March 2015, the medicinal health product regulatory agency MHRA released a new guide on “GMP Data integrity definition and guidance for industry” these regulatory set deadlines to comply with the Data integrity issue up to the end of 2017.
Later in April 2016, FDA released “Data integrity and compliance with cGMP guidance for industry,” but surely there has been guidance for good manufacturing practices according to 21CFR (210 211 and 212). Data integrity issues were mentioned, but because of the lots of regulatory issues and every new update, more focus on it.
Conclusion
Recently data integrity issues are rising more and more on the daily basis, because Regulatory bodies are more focused on real data, by use of more and more tools and systems, it gets more complicated since the impact of data integrity is paying off high cost. It is something that has a high priority.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
There is a total of 9 principles for ALCOA and ALCOA+
Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate.
Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available
No, Data integrity is good, but Data integrity issues are bad for any Pharmaceutical industry.
Related useful references
21 CFR Part 11, Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures:
http://www.fda.gov/RegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm125067.htm
MHRA GMP Data Integrity Definitions and Guidance for Industry, March 2015:
https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/412735/Data_integrity_definitions_and_guidance_v2.pdf
Data Integrity and Compliance With CGMP Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE, April 2016:
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm495891.pdf
FDA warning letters are public and can be found here:
http://www.fda.gov/ICECI/EnforcementActions/WarningLetters/default.htm

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].

