Deviation from any process in pharmaceuticals can lead to a matter of investigation and root cause analysis. the manufacturer or responsible person shall be followed the following steps to do an investigation and root cause analysis by using corrective and preventive action.
1. Investigation/ Title for Root Cause Analysis:
Start with the product’s name and what was the observation, for eg. the weight of good tablets which is destroyed during the compression stage but not recorded in batch records.
2. Investigation Team:
There shall be a team involved in the investigation with name, department, and designation.
3. Behind the scenes for event investigation:
Use the 5 WHYs technique for investigation and root cause analysis.
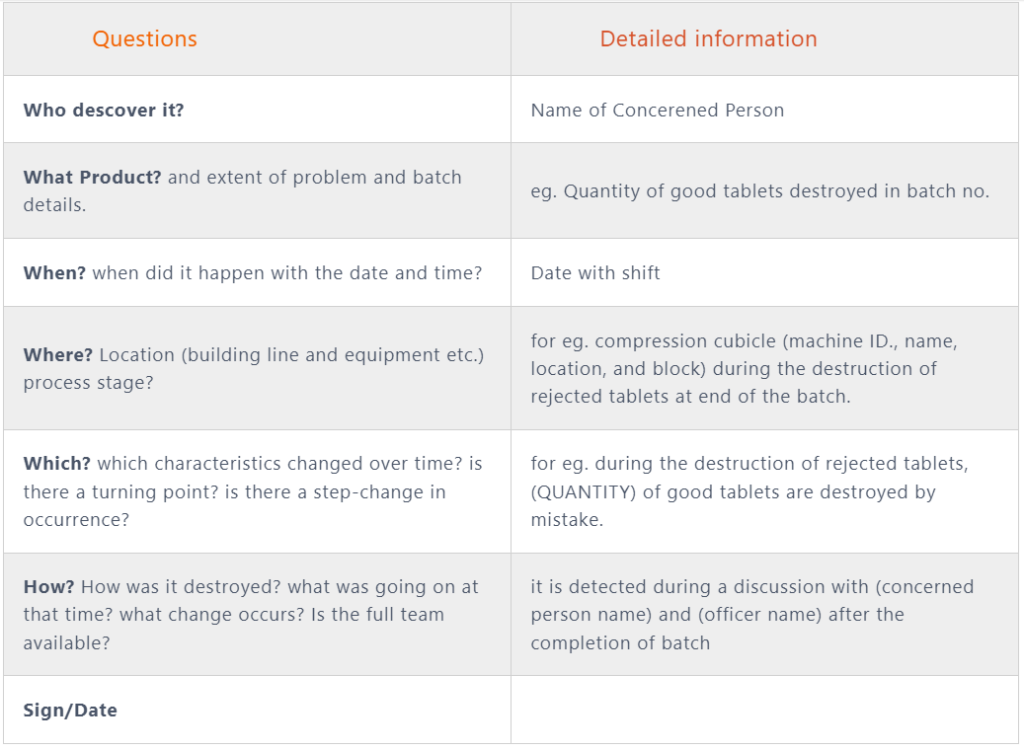
4. Investigation requirements:
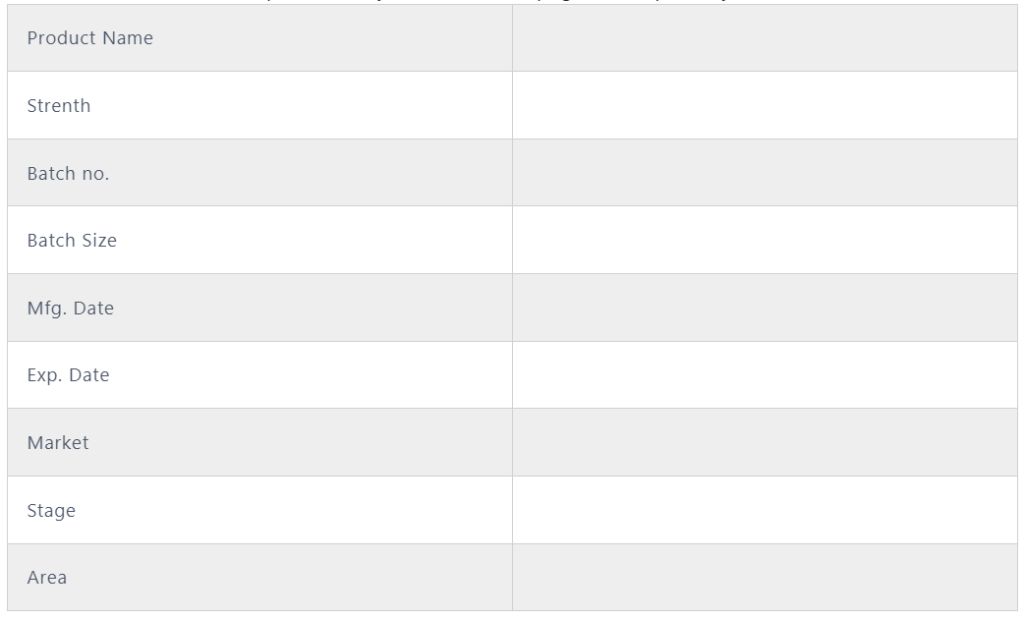
A. Gather the information GEMBA:
- Write the details of the information like product manufacture location, machine name, batch start date and time, officer, and batch size.
- Calculate the no. of good tablets compressed and the remaining quantity of good tablets destroyed, and others destroyed, then a further match with BMR Records. proceed with an investigation if found any variation.
- Further, write the details about the name of the officer and operation activity (date and start time). during operation how much quantity was destroyed and who checked and verified by as per label affix? write the observation and fault or gap details.
5. Define:
A. Problem statement: (wt. of tablets in kg) which is destroyed during the compression stage but not recorded in batch records with batch no. mention.
B. Process mapping: line clearance- machine setting-startup- compression operation-destruction of rejected tablets- reconciliation- Review BMR.
6. Measure:
Write about what is to be measured if not then do NA.
7. Analysis for Root Cause:
Analysis of the reported event is done with why-why analysis.
WHY: Why quantity? of good tablets destroyed
Ans: Quantity? of tablets separated for the sample are taken destruction along with rejected tablets of the batch.
WHY: Why good tablets are taken along with rejected tablets for destruction?
Ans: After completion of the operation good tablets and rejected tablets were in a cubicle. due to the small number of good tablets, these tablets are taken with rejected tablets for destruction by the concerned person’s name. the person destroyed the tablets by putting water in them inside the wash area and transfer to ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) for further disposal.
7.a. Potential root cause based on the assessment performed:
Potential root cause based on the assessment performed from the BMR review and discussion with the concerned officer, it is observed that after the completion of the operation good tablets were separated for sampling as well as rejected tablets were kept in a cubicle. quantity of rejected tablets was checked by a concerned officer and QA officer. during the transfer of rejected tablets for destruction production officer took the good tablets along with rejected ones and destroyed the tablets by mistake.
8. Impact assessment:
- The batch closed as per the destruction record and reconciliation done
- The stock adjustment will be done for WIP of (quantity of tablets).
9. Improve and control (CAPA):
Awareness training regarding the event shall be imparted to all officers.
10. Conclusion for Root Cause Analysis:
To conclude the investigation includes the summary in short likes; at the end of the operation concerned officer destroyed the good tablets kept in the sample along with rejects generated during the operation, and the mistaken quantity of these tablets is not recorded in BMR.
The stock adjustment will be done for WIP of (quantity of tablets).
Note: Include the formate number for root cause analysis.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
