In pharmaceutical analysis, a limit test is a type of analytical test used to determine impurity in a substance whether a substance is present in a sample at a concentration above or below a specified limit. Limit tests are often used to ensure that a substance meets certain quality standards or regulatory requirements.
Definition
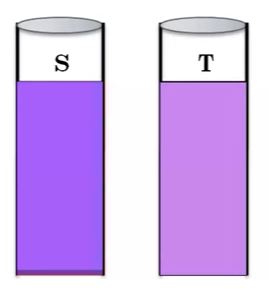
The limit test involves the simple comparison of opalescence, turbidity, or color with a fixed standard.
The Technique used for the Limit test
Limit tests are typically performed using specific analytical techniques, such as spectroscopy, chromatography, or titration. These techniques are used to accurately measure the concentration of the substance in the sample, and the results of the test are compared to the specified limit to determine whether the substance is present in the sample at an acceptable level.
Types of Limit test
Limit tests are basically three types:
- Test in which no invisible color
- Comparison Methods
- Quantitative Determination
Quantitative: A quantitative limit test is a laboratory test used to determine the how much concentration of a specific substance in a sample. It is often used in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure that the levels of active ingredients in a drug meet the specifications set by regulatory agencies.
Usage of Limit test
Limit tests are used in a variety of contexts in the pharmaceutical industry, including the testing of raw materials, finished products, and in-process materials. They are an important part of the quality control process in pharmaceutical manufacturing and are used to ensure that products meet the required standards of purity, potency, and safety.
Importance of Limit test
Limit tests are important in the pharmaceutical industry because they help to ensure the quality and safety of drugs and other products. By establishing limits for certain substances, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet regulatory requirements and are suitable for their intended use.
Limit tests can be used to verify that a substance meets certain quality standards, such as those set by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) or the European Pharmacopoeia (EP). These standards establish limits for various impurities and contaminants that may be present in pharmaceutical products, and limit tests are used to ensure that these substances are present at acceptable levels.
In addition to verifying the quality, limit tests can also be used to identify and quantify contaminants that may be present in a sample. This is important because some contaminants can pose a risk to human health if present in high concentrations. By performing limit tests, manufacturers can ensure that their products do not contain harmful levels of contaminants and that they are safe for use.
Overall, limit tests are an essential part of the quality control process in the pharmaceutical industry, and play a vital role in ensuring that drugs and other products are safe and effective for use.
Various types of Limit tests as per specific Substance
There are many different types of limit tests that can be used in the pharmaceutical industry, depending on the specific substance being tested and the analytical technique being used. Some common examples of limit tests that are used in the pharmaceutical industry include:
Heavy metals limit test: This test is used to determine the concentration of heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, in a sample. It is often used to ensure that raw materials and finished products do not contain harmful levels of these substances.
Residual solvent limit test: This test is used to determine the concentration of residual solvents, such as ethanol and acetone, that may be present in a sample. It is important because some residual solvents can be toxic if present in high concentrations.
Microbial limit test: This test is used to determine the concentration of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, in a sample. It is important because some microorganisms can cause infections or other health problems if present in high concentrations.
Assay limit test: This test is used to determine the potency or concentration of a specific active ingredient in a sample. It is important because it helps to ensure that a product contains the correct amount of the active ingredient.
Impurity limit test: This test is used to determine the concentration of impurities, such as degradation products or contaminants, in a sample. It is important because some impurities can affect the quality or safety of a product.
These are just a few examples of the many types of limit tests that are used in the pharmaceutical industry. Other types of limit tests may include tests for pH, moisture content, and other properties that are important for the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Apparatus used for Limit test
For the determination of the limit test, the Following apparatus is used:
- Nessler Cylinder: Borosilicate glass which is colorless has uniform walls and diameter throughout the height.
- Pipette
- Glass rod
The solvent used in the Limit test
Solvents are used in a variety of applications in the pharmaceutical industry, including in the production of drugs and other products, and in the testing of raw materials and finished products. Solvents are often used in limit tests to dissolve samples and prepare them for analysis.
The specific solvent used in a limit test will depend on the substance being tested and the analytical technique being used. Some common solvents used in limit tests in the pharmaceutical industry include:
Water: Water is a universal solvent and is often used to dissolve a wide variety of substances. It is often used in limit tests because it is relatively inexpensive and easy to obtain.
Alcohols: Alcohols, such as ethanol and methanol, are commonly used as solvents in the pharmaceutical industry. They are often used to dissolve and extract compounds from plant materials and are also used in the production of medications.
Acetone: Acetone is a common solvent used in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for the production of drugs and other products. It is a powerful solvent that can dissolve many different substances, and is often used in limit tests to prepare samples for analysis.
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO): DMSO is a polar solvent that is often used to dissolve and extract compounds from plant materials. It is also used in the production of drugs and other products and may be used in limit tests to prepare samples for analysis.
It is important to select the appropriate solvent for a limit test, as the choice of solvent can affect the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
Details Examples of Limit test:
- Limit test for Iron
- Limit test for Sulphate
- Limit test for Lead
- Limit test for Chloride
- Limit test for Arsenic
Related: Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 N HCl

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
