The Limit Test for Sulphate is designed to determine the allowable limit of Sulphate contained in a sample.
Principle:

The principle for the limit test of Sulphate is based on the reaction of soluble Sulphate with barium chloride in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid to form barium Sulphate which appears as turbidity with a white precipitate.
Then a comparison of turbidity is done with standard turbidity obtained from a known amount of Sulphate and the same volume of dilute hydrochloride acid have been added to both solution.
The barium chloride test solution in the IP has been replaced by barium Sulphate regent which has barium chloride, Sulphate-free alcohol, and a solution of potassium Sulphate (K2SO4) has been added to the solution to increase the sensitivity of the test.
Read Also: Limit test in Pharmaceuticals; Limit test for Iron and Chloride
Apparatus Required for Sulphate Limit Test:
- Nessler cylinders
- Glass rod
- Stand
Chemical Required:
Barium sulphate reagent: Preparation: 0.05 M barium chloride solution is prepared by dissolving 12 g of barium chloride in 1000ml of water, Now take 15 ml of the prepared solution and add 55 ml of water, 20 ml of alcohol and 5 ml of 0.0181% w/v solution of potassium sulphate and the final volume was made upto 100 ml.
Reaction:
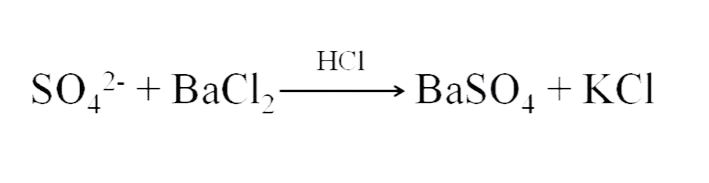
- Hydrochloric acid helps to make the solution acidic.
- K2SO4 has been added to the solution to increase the sensitivity of the test by releasing ionic concentration in the reagent.
- Alcohol helps to prevent supersaturation.
Procedure for Limit Test for Sulphate:
| Test Sample | Standard Compounds |
|---|---|
| The specific weight of the compound is mixed in H2O or the solution is prepared as described in the pharmacopoeia and transferred in the Nessler cylinder. | Take 1 ml of 0.1089 % w/v solution of potassium Sulphate in the Nessler cylinder. |
| Add dilute HCL of about 2 ml. | Add dilute HCL of about 2 ml. |
| Dilute to 45 ml in the Nessler cylinder. | Dilute to 45 ml in the Nessler cylinder. |
| Add 5 ml of barium sulfate reagent. | Add 5 ml of barium sulfate reagent. |
| Keep it stagnant for 5 minutes and observe the turbidity | Keep it stagnant for 5 minutes and observe the turbidity |
Barium Sulphate reagent contains barium chloride, Sulphate-free alcohol, and a small amount of potassium sulfate.
Observation:
The turbidity or white precipitate produced in the tested sample solution should not be more than the standard solution. if turbidity produced in the sample solution is less than the standard solution, the sample will pass the limit test of Sulphate.
Reasons:
Hydrochloric acid helps to make the solution acidic. Potassium sulphate is used to increase the sensitivity of the test by giving ionic concentration in the reagent.
Alcohol helps to prevent supersaturation and so produces a more uniform opalescence.
Referernce:
The Indian Pharmacopeia

Panks Pamyal is a Author and Editor at Pharmaguddu.com. He Worked in Top Pharmaceuticals MNCs in India had a more then 10 years experience in Quality control department. He Delivering most valuable insights and knowledge through this website.
