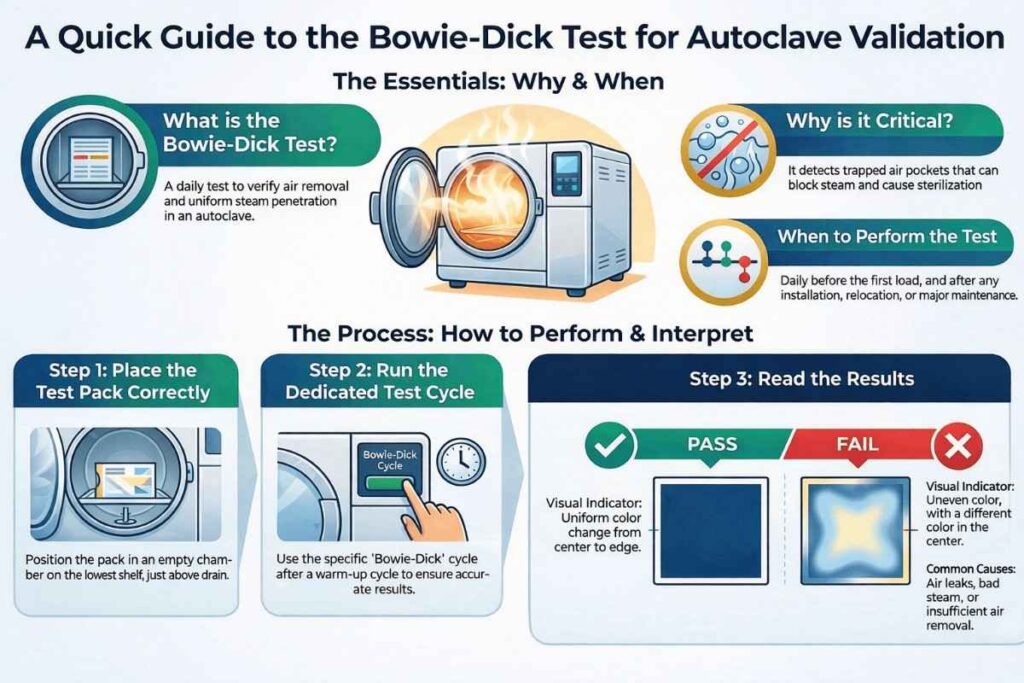
The penetration of steam into all parts of the autoclave is essential for achieving and maintaining effective sterilization. The Bowie–Dick test is performed to verify adequate air removal and uniform steam penetration within a pre-vacuum steam autoclave, using a standardized Bowie–Dick test pack.
During sterilization, air pockets and non-condensable gases may remain trapped inside the chamber or load. These can block steam penetration and lead to false sterilization results. The Bowie–Dick test helps detect such conditions and is therefore a critical part of autoclave validation and routine monitoring in pharmaceutical industries.

A Quick Guide to Bowie-Dick Autoclave Test:
Principle of Bowie–Dick Test:
Principle:
The test is based on a Class 2 chemical indicator, typically arranged in the form of a St. Andrew’s cross, fixed on paper or card and placed inside a porous test pack. The indicator responds to a defined combination of time, temperature, and steam moisture.
A uniform color change across the indicator confirms effective air removal and steam penetration. Any uneven or incomplete color change indicates the presence of residual air or non-condensable gases.
How to Perform a Test Pack?
To perform this test, Run a test for about 240 seconds, known as the bowie dick cycle. Keep folded huckaback towels at the center of the chamber Indicator and then subject them to an operating cycle in an empty chamber.
The indicator tape starts to show a change in color in response to a combination of time, temperature, and moisture. A change in the sheet color pattern was used to determine the test result. The chamber must be empty during the test, and only the Bowie Dick test pack should lie inside it.
Frequency of Bowie–Dick Test (GMP Requirement):
The Bowie–Dick test shall be performed:
- Daily, at the start of each working day
- Before the first sterilization load
- In an empty chamber of a pre-vacuum autoclave
Additional testing is required:
- After installation, relocation, or major maintenance
- After a failed sterilization cycle
- During Operational Qualification (OQ) and Performance Qualification (PQ)
This frequency is aligned with:
- EU GMP Annex 1 (Clause 8.61) – daily air-removal test
- ISO 17665-1 – routine Bowie–Dick testing before use
- FDA GMP expectations (industry best practice)
- WHO GMP requirements for sterilizer monitoring
How to Perform the Bowie–Dick Test:
To perform the test, run a Bowie–Dick cycle of approximately 240 seconds after a warm-up cycle. The chamber must be completely empty, except for the Bowie–Dick test pack.
Place the test pack:
- On the lowest shelf, directly above the chamber drain
- Ensure correct positioning, as this is the most challenging location for air removal
The indicator changes color in response to sterilization conditions. The result is determined by observing the color pattern and uniformity of the indicator sheet.
Procedure for Autoclave Validation:
Before performing the Bowie–Dick test, a warm-up cycle is recommended to stabilize chamber temperature and prevent condensation. Improper air removal may otherwise give misleading results.
Steps:
- Place the standard test pack with indicator paper at the center of the pack
- Position the pack at the base supports of the chamber, 100–200 mm above the floor
- Select the Bowie–Dick test cycle
- Ensure the holding time does not exceed the specified limit
Excessive exposure time may cause complete color saturation, making it difficult to detect failed conditions.
Bowie–Dick Test Operation and Interpretation:
Record the chamber temperature and pressure during the holding phase and until the end of the cycle. After completion:

- Remove the indicator paper
- The test is satisfactory if the color change is uniform throughout
- Any visible difference between the center and corners indicates a failed test
Failed results must be documented, investigated, and corrected before using the autoclave for production.
The indicator paper should be:
- Marked with the test result
- Retained for at least 3 months
- Associated sterilization records retained as per GMP (typically 11 years)
Common Causes of Bowie–Dick Test Failure:
- Insufficient air removal
- Air leaks during vacuum phase
- Presence of non-condensable gases in steam
- Leakage in chamber or piping system
Solutions for Bowie–Dick Test Failure:
- Air leak: Perform a vacuum leak test
- Inadequate warm-up: Run a 5-minute sterilization cycle before the test
- Incorrect placement: Ensure the test pack is positioned above the drain point
Guidelines for Test Pack Composition:
The traditional Bowie–Dick test pack consists of:
- Folded 100% cotton surgical towels, freshly laundered, not ironed
- Towels folded to at least 9 × 12 inches (23 × 30 cm)
- Pack height: 10–11 inches (25–28 cm)
- Weight: approximately 7 kg
- A commercially available Bowie–Dick test sheet placed at the center
- Wrapped loosely with 100% cotton fabric (140 thread count, two-ply)
Innovation in Autoclave Validation:
SteriSense is an electronic Bowie–Dick test device that provides real-time and depth-wise information on sterilization parameters. It allows electronic data storage and complies with ISO 17665 requirements.
Advantages of SteriSense in Bowie–Dick Testing:
- Eliminates false or borderline results
- Electronic documentation and easy data retrieval as per ISO 17665
- Accurate comparison of test cycles
- Replaceable Process Challenge Device (PCD)
- Supports multiple test cycles with minimal cooling time
Process challenge device (PCD) may be a unique advantage of being replaceable, permitting several test cycles in a row with minimal need for cooling. Its patent is under process.
Related Topics:
- Difference between Humidity and Relative Humidity
- Moisture Content and Loss On Drying (LOD) in Pharmaceuticals
- pH Meter | Principle, Calibration, and Working
- Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) in Pharmaceutical
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Injectable | Parenteral | sterile preparations, types, Standard test
- Tablet Friability Test Calibration and Specification
- Pharmaceutical Sampling, types, tools ( Guidelines)
- Vernier Caliper measurement and operation in Pharma
- Handling of Laboratory Incidents in Pharma
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Ans: A leak test is performed to check the airtightness of the vacuum autoclave chamber.
A leak test is to check the airtightness integrity of the chamber and plumbing system. The frequency of autoclave leak tests should be done at least weekly in an empty chamber to ensure the airtightness of the pre-vacuum steam sterilizer. It must be performed if the Bowie Dick test fails.
Ans: DART (Daily Air Removal Test) is widely used for the Bowie Dick test. It is a light pack for fast use. So place the dart test pack on the lowest shelf over the drain point to remove air during the vacuum phase of the cycle through the chamber of the dart test.
Steam will enter the chemical indicator chamber during the exposure phase, and then open the door to see immediate results.
Ans: If the indicator line turns black, it is good to pass the test, showing that air is removed completely. If failure, all bars will not turn black.
Ans: The Temperature must be specified to kill microorganisms, and the standard temperatures are 121 °C and 132 °C. Temperatures must be maintained to kill all forms of microorganisms.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].

WHICH CHEMICAL USED IN BOWIE DICK KIT
Thermochromatic ink