Here is a detailed discussion on How to Prepare and Standardization of Potassium Permanganate (1M, 0.1M, 1N, 0.1N) solution by using different reagents in Labs.

Preparation and Standardization of 1M Potassium Permanganate
Potassium permanganate – M.Wt – 158
Preparation of 1M Solution of Potassium Permanganate:
- Dissolve an accurately weighed 158 gm of KMnO4 in 900 ml of water.
- Heat it in a water bath for 1 hour, cool it, then filter it using a sintered glass filter.
- Add enough water to make it 1000 ml.
Principle: In volumetric analysis, many reactions involve oxidation and reduction. An oxidizing agent is estimated by titrating with a reducing agent and vice versa. These titrations are called redox titrations. Standardizing KMnO4 is an example of a redox titration. KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent and, in an acidic medium, it oxidizes oxalic acid to CO2.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2C2O4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O + 10CO2
The temperature is maintained at 60˚-70˚ C during titration because the reaction is slow at room temperature. No indicator is needed as KMnO4 is a self-indicator.
Preparation of 1M Oxalic Acid Solution: Dissolve an accurately weighed 126.07 gm of Oxalic acid in enough water to make 1000 ml.
Procedure for Standardization of 1M KMnO4:
Pipette out exactly 10 ml of 1M Oxalic acid solution into a clean conical flask. Add 10 ml of diluted H2SO4. Warm the flask contents to 70˚C and titrate with KMnO4 solution. Continue titration until a faint pink color appears. Repeat for concordant values and record in a table.
Calculation of Molarity of KMnO4:
Use the formula M1V1 = M2V2
where V1 = Volume of 1M Oxalic acid solution (10 ml)
M1 = Molarity of Oxalic acid solution (1M)
V2 = Volume of KMnO4 solution used (from the average burette reading)
M2 = Molarity of KMnO4 (To be Find Out).
Calculate M2=
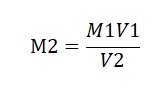
Preparation and Standardization of 0.1M KMnO4:
To make 0.1M Potassium Permanganate, follow these steps:
- Take 15.8 grams of KMnO4, put it in 900 ml of water, and heat it in a water bath for an hour.
- Let it cool, then filter it with a sintered glass filter.
- Add enough water to make it 1000 ml.
Principle: In a Lab, when we analyze volumes, we often deal with oxidation and reduction processes. Oxidizing agents are measured by titrating with reducing agents, and vice versa. This type of titration is called redox titration. Standardizing KMnO4 is an example of redox titration. KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent; in an acidic environment, it turns oxalic acid into CO2.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2C2O4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O +10CO2
During the titration, keep the temperature between 60˚-70˚ C, because the reaction is slow at room temperature. KMnO4 itself serves as an indicator, so no additional indicator is needed.
Preparation of 0.1M Oxalic Acid Solution: Dissolve 12.6 grams of Oxalic Acid in enough water to make 1000 ml.
Standardization of 0.1M KMnO4:
- Take exactly 10 ml of 0.1M Oxalic Acid, put it in a clean flask, add 10 ml of dilute H2SO4, warm it to 70˚C, and titrate with KMnO4.
- Keep titrating until you see a faint pink color.
- Repeat for consistent results and record them in a table.
Use the formula M1V1 = M2V2 to calculate the Molarity of KMnO4:
V1 (Volume of Oxalic Acid) = 10 ml
M1 (Molarity of Oxalic Acid) = 0.1M
V2 (Volume of KMnO4) = Average Burette Reading
M2 (Molarity of KMnO4) =?
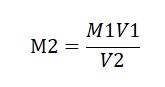
Preparation and Standardization of 1N Potassium permanganate :
To make a 1N Potassium permanganate solution, follow these steps:
- Take 31.6 grams of KMnO4 and dissolve it in 900 ml of water.
- Heat the mixture in a water bath for an hour, let it cool, then filter it using a sintered-glass filter.
- Finally, add enough water to obtain the total volume to 1000 ml.
Principle: In volumetric analysis, certain reactions involve oxidation and reduction. We estimate the strength of an oxidizing agent by titrating it with a reducing agent and vice versa. These titrations are known as redox titrations. The standardization of KMnO4 is an example of a redox titration. KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent, and in an acidic medium, it oxidizes oxalic acid to produce CO2.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2C2O4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O +10CO2
The titration should be performed at a temperature of 60-70˚ C because the reaction is slow at room temperature. No indicator is needed as KMnO4 acts as a self-indicator.
Prepare 1N Oxalic Acid Solution: Dissolve 63.035 grams of Oxalic acid in enough water to make 1000 ml of solution.
Standardize 1N KMnO4 with Oxalic Acid:
- Pipette exactly 10 ml of 1N Oxalic acid solution into a clean flask.
- Add 10 ml of diluted H2SO4. Warm the mixture to 70˚C and titrate with KMnO4 solution.
- Stop titrating when a faint pink color appears.
- Repeat the titration for consistent values, recording them in a tabular form.
We use a formula – N1V1 = N2V2 – to figure out how strong our potassium permanganate is.
N1 is the strength of oxalic acid (it’s 1N).
V1 is the amount we used (it’s 10 ml).
N2 is what we’re figuring out.
V2 is how much potassium permanganate we used (To be Calculated).
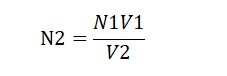
Preparation and Standardization of 0.1N Potassium permanganate :
Potassium permanganate – M.Wt – 158
Potassium permanganate has a molecular weight of 158. Below is the process of how you can make a 0.1N solution:
- Take 3.16 grams of KMnO4 and dissolve it in 900 ml of water.
- Heat it in a water bath for an hour, let it cool, then filter it using a special filter.
- Add enough water to make it 1000 ml.
Now, in simple terms, we often use a process called redox titration to figure out the amount of one substance by reacting it with another. In this case, we’re standardizing KMnO4, which is a strong oxidizing agent.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 + 5H2C2O4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 8H2O +10CO2
During the process, we keep the temperature at 60-70°C, because the reaction is a bit slow at room temperature. No need for an indicator as KMnO4 acts as an indicator.
Preparation of 0.1N solution of oxalic acid: Make a 0.1N solution of oxalic acid by dissolving 6.3 grams in enough water to make 1000 ml.
Standardization of 0.1N Potassium permanganate:
- Take exactly 10 ml of this oxalic acid solution in a flask, add 10 ml of dilute sulfuric acid, warm it to 70 degrees Celsius, and titrate it with KMnO4 solution until you see a faint pink color.
- Repeat this process for accuracy and record your values in a table.
To find the normality of KMnO4, use the formula: N1V1 = N2V2.
Here, V1 is the volume of the oxalic acid solution (10 ml)
N1 is its normality (0.1N)
V2 is the volume of the KMnO4 solution used
N2 is what we want to find.
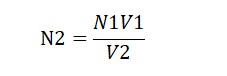
Next, Preparation and Standardization of 0.02M Potassium Permanganate “Will Update soon”
Read More:
- 0.1 M KOH Solution Preparation and Standardization
- 0.1 M Sodium Nitrite Preparation and Standardization
- 0.05 M EDTA Solution Preparation and Standardization
- Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 M Ceric Ammonium Sulphate
- Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 M Disodium Edetate (EDTA)
- How can I Prepare and Standardize 0.5 M Sulfuric acid?
- 1.0 M Sulfuric Acid Solution- Preparation, Standardization, Reagents, Formula
- 0.1 M Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), Preparation and Standardization
- Preparation and Standardization of 1 M Sodium Hydroxide Solution (NaOH)
- Preparation and Standardization of 1.0 M Hydrochloric Acid
- Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 N HCl

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].
