Compression machines are used to compress the powder or granules into uniform size and weight. The machine and its tools are key in this process. Therefore, taking good care of and lubricating these tools is extremely important in the pharmaceutical industry.

You may also read: about Tablet defects, Capsule defects, and Solid dosage form
Different Types of Parts in Compression Machine:
The tablet Compression Machine has the following functional parts:
1. Hopper:

A hopper is provided at the top of the compression machine to hold or supply the bulk granules/powder to the feeder.
2. Feeder:

The feeder feeds the granules/powder from the hopper to the dies.
3. Punches:

Punches travel to the die to compress the powders within the dies.
4. Dies:

Dies are used to specify the size and shape of the tablets.
5. Turrets:

Turrets help in holding upper punches and lower punches.
6. Cams:

Cams help to guide the movements of punches.
7. Compression Rollers:
Compression machine rollers push the punches toward the die to form the tablets.
8. Take off blade:
It is adjusted just in front of the feeder box to carry out the compressed tablets to the discharge tube.
9. Discharging chute:

The discharging chute provides the path for tablets to travel to a Metal detector/ collection bin.
10. HMI:
HMI is a functional part of the machine where all the parameters are set before the process.
Different Stages in the Tablet Compression Process?
1. Filling: Granules flow through compression tools like a punch, dia, and cavity, which are responsible for the filling of the granules according to the position of lower punches to make tablets. The filling volume size is adjusted as per the requirement.
2. Metering: Metering is the process of removing extra granules from the turret. The metering cam is responsible for controlling the Height of the lower punch, which helps in controlling the volume of granules.
3. Compression: Compression is the formation of tablets by approaching the top and bottom punch to come together by pressure within the die, resulting in the deformation of particles like Elastic deformation and plastic deformation.
4. Ejection: Ejection is the removal of tablets from the die wall by raising of lower punch. If there’s not enough lubrication, it makes it harder to eject them. This leads to issues like sticking and picking.
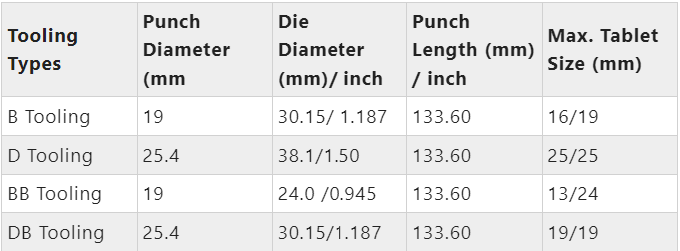
Type of Tooling in Compression Machine?
The arrangement or Setup of dies and punches on the machine for compressing tablets is known as tooling.
There are different types of compression machines and tooling, based on the sizes of punches and dies as follows:
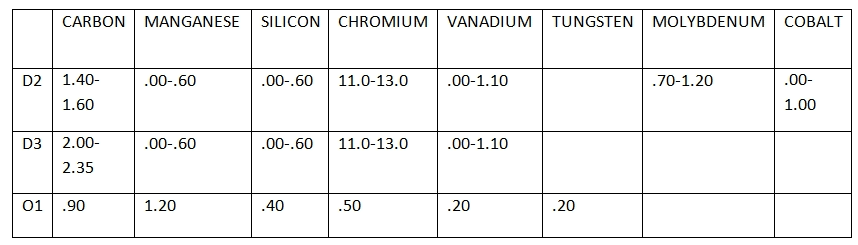
Chemical Composition of Tools:
The chemical Composition of the Tools used for the compression machine is as below:
Punch and Head Terminology:
Punch:
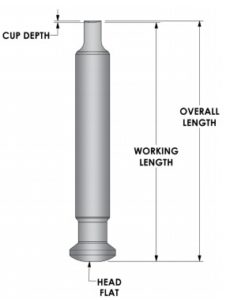
- Head: The head is the end part of a punch that guides it through the cam track of the compression machine.
- Head Flat (Dwell Flat): The upper surface of the punch, which is flat, receives the compression force from the roller (in upper punches) and determines the ejection height and weight (in lower punches).
- Outside Head Angle: The area touched by a roller during compression.
- Inside Head Angle: An area that assists in pulling down the lower punches after ejection and lifts upper punches after compressing tablets.
- Neck: It’s the region between the head and barrel, providing a path for the cam.
- Barrel: Guides the punch while it travels up and down.
- Stem: The area from the lower side of the head that extends to the full diameter of the barrel.
- Tip: The lowest portion of the punch, determines the profile of the tablet.
- Tip Face: The region where tablets are formed; a good quality finishing is necessary for high-quality tablets.
- Working Length: The working length of the punch is the distance from the head flat to the lowest measurement area of the punch cap.
- Overall Length: It is the length from the punch tip to the head flat.
- Key Angle: Influences the tablet shape and turret rotation.
- Domed Heads: Responsible for tablet hardness and quality, enhancing dwell time.
- Dwell Time: It is the travel time of the punch head over the compression roller.
- Hardness: Measured in HRC (Rockwell ‘C’ scale).
- Clearance: Clearance= Die bore dia-punch tip dia.
Die Terminology for Tablet Compression:
- Die. O.D.: is the outside diameter of the die, which is fitted with the die pocket in the compression press.
- Die Height: is the overall Height of the die from top to bottom.
- Die Bore: Die Bore is the part of the die where the tablet forms; it determines both the shape and size of the tablets.
- Chamfer: is the entry angle of the die bore.
- Taper Dies: They are single (one side wider at the opening face) and double taper dies (both sides wider upper and lower) for easy ejection and to prevent capping and delamination problems)
- Die Groove: The groove outside the periphery of the die, which helps in fitting the die in the press.
- Lined Dies: it’s also called Insert dies; these dies are fitted with a linear insert made from the materials of tungsten carbide and ceramic.
Latest Advancements in a Compression machine
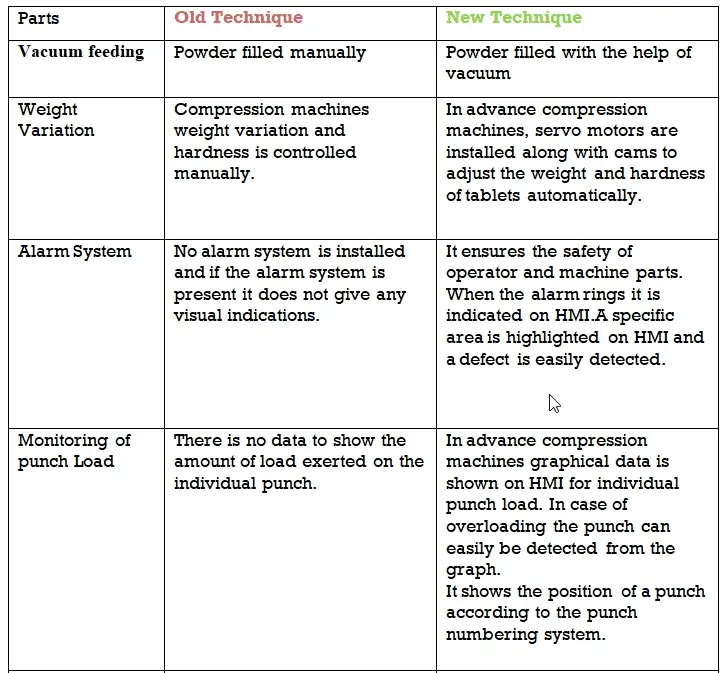

The Life span of the Dies and Punches:
The life span punches and dies depending on MOC( materials of construction) as Follows:
- OHNS Punches and HCHC Dies- 4 Million tablets
- HCHC Punches and HCHC Dies- 7.5 Million tablets
- Complete hard chrome plating punches and HCHC dies- 8.5 Million tablets.
Punches and Dies: Cleaning lubrication, Wear and Tear, and Storage:

1. Cleaning: use 0.1% teepol solution with purified water for cleaning after the use of punches and dies, also using a soft plastic scrubber if required.
Caution: Do not use a metal scrubber; it will make scratches and marks, roughness on punches, and dies.
- Rinse the punches and dies finally two to three times with hot purified water if required to do the streaming for cleaning.
- After cleaning, intimate to the QA department for rinse water or swab sample to QC for testing for a residual trace of detergent and previous product ( Method and the cycle of cleaning of punches and dies shall be validated).
- Use oil-free filtered compressed air and a suitable dry clean duster for the dry. after cleaning and drying, the disinfection of punches can be done by wiping with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
- Allow to dry the punch and then lubricate the punches before storing. Polishing can also be done by using a polishing kit.
2. Lubrication: Lubrication is done by using food-grade oil like castor oil or liquid paraffin, but there is a problem with the rancidity of the oil. So nowadays, various synthetic lubricants and grease are available, which have been now used in most pharmaceutical companies.
Now some of the varieties of synthetic oil and grease, which are 100% synthetic and non-toxic, are listed in NSF and USFDA authorized. components are in accordance with FDA regulation 21CFR 178.3570
Names of some grease and oil are:
- ET- 2S grease
- ET- 10S,20S,90S,140S Lubricants
- HT- 1000G, High temperature, and non-melting grease
- Store the punches and dies in their dedicated cabinet ( made of a soft material to avoid damage to punches and dies) after proper greasing.
- Handle punches and dies carefully to increase their life.
- After usage, wipe the punches and dies with a proper clean and dry lint-free duster with IPA 70%, then allow them to dry.
3. Wear and Tear of punches and dies: Regularly inspect the punches and dies for any damage and polish them if they show signs of wear and tear. To do this, follow the guidelines and use a punch inspection and maintenance kit. Skilled, experienced, and knowledgeable individuals should handle the inspection and maintenance of punches and dies records.
Compression machine kit for punches and dies:
- Motorized chuck: The motorized chuck is used for cleaning, and polishing of concave, the plane also punches for the cleaning of the punch tip, punch barrel, and punch head.
- Double-ended Polisher: Double-ended polishers are used for cleaning, and polishing of all types of embossed punch tips, including break lines and shaped punch tips.
- High-speed Grinder: A High-speed Grinder is used for polishing plain concave punches and die bores.
- Bench comparator: Bench comparator used for measurement and comparison of punch length, checking of punch tip, to barrel concentricity.
- Lapping sticks: Used for Final Polishing
- Fine polishing strip: use for light polishing (grit 320 and 600)
- Emery rolls: Used for polishing the punch head with 180 grit for general polishing and 320 grit for lighter polishing.
- Lapping stone: Utilized to remove burrs from the punch tip.
- Nylon brushes: Employed with a double-ended motor to polish embossed punch tips, flat beveled and shaped punch tips, and for cleaning break lines.
- Micro-polishing paste: Used for micro-polishing.
- Chalk powder: Applied for drying off the polishing compound from the punch tip.
- Lubricants: Used for lubrication.
- Brass wheel.
- Turret brushes: Utilized for removing powder.
- Cotton wool: Used for cleaning.
- Magnifying Glass: Used for inspection.
- Punch holder: Employed to protect the punch from wear and tear.
- Length gauge: Used for checking all lengths (screw gauge and digital vernier caliper).
Punches wear and tear:

- Check for overall length; it should be within specified limits.
- The inside head angle should not be worn out due to friction on the cam, and it should be smooth.
- The flathead should be smooth
- Body diameter should be within limits
- The punch tip should be smooth and not worn out due to friction, and it should be intact and not damaged.
- The embossing letter and break line height and uniformity should be sharp and intact; it creates a problem during tablet ejection from dies, if not proper.
Dies, Tears and wear:
- The outer diameter should be within limits.
- inside the cavity, the finishing should be mirror-finished and smooth,
- The height of the die should be within the limits
- Die grooves should be smooth and not damaged.
- The Die chamber should be proper, smooth, and appropriate; otherwise, it creates a problem in tablet ejection.
References:
- Pharma Pathway Book edition 2016.
- Wikipedia
Related Topics:
- How to Check Sieve/ Screen Mesh Size | Sieve Calibration
- Double Cone Blender; Principle, Working, and Applications
- 6 Steps Sugar Coating of Tablets: Process, Materials usage, Defects and Remedies
- Filling Procedure for Vaccine in Pharmaceutical
- Equipment Capacity Calculation and Factor affecting in industries
- Granulation Technique in Tablet Manufacturing
- Calculation for Capacity of Tablet Coating Machine With Example
- Hammer Mill; Usage, Construction, Working Principles, and Types
FAQs on Compression Machines and Tooling
Ans: A compression machine compresses powder or granules to form uniform tablets.
Ans: Maintenance and lubrication of tooling are critical for tablet compression machines.
Ans: Essential parts include hopper, feeder, punches, dies, turrets, cams, and more.
Ans: Tablets are formed through filling, metering, compression, and ejection stages.
Ans: Tooling involves setting up dies and punches for tablet compression on the machine.
Ans: Lubrication is done using synthetic oils and greases like ET-2S, HT-1000G, and more.
Ans: Proper cleaning, lubrication, and careful handling contribute to an extended lifespan.
Ans: Clean with teepol solution, avoid metal scrubbers, rinse with purified water, and disinfect with isopropyl alcohol.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].

Very informative.