0.1 M Silver Nitrate Solution Preparation and Standardization
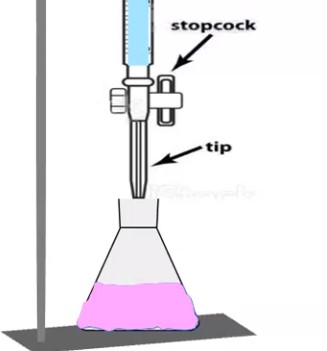
Aim: Preparation and Standardization of 0.1 M Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) solution by using sodium chloride in Pharmaceutical Labs. Name: 0.1 M Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) Reagents used to Prepare and Standardization of 0.1 M AgNO3 : Glassware: Volumetric Flask, measuring cylinder, Burette, Conical Flask, beaker, and Pipettes. Principle: In the lab, we used a process where … Read more