Quality assurance plays an essential role in manufacturing high-quality pharmaceutical products. It is the aspiration of many to secure positions within the quality department. To achieve this goal, individuals must be successfully guided to excel in interviews. To aid in this industry, we have curated a list of 100+ Quality Assurance Interview Questions suitable for both entry-level and experienced candidates. We trust that these questions, focusing on Quality Assurance/IPQA, will guide you toward realizing your career aspirations in the pharmaceutical industry.

QA Interview Questions for Fresher and Experienced
Q.1 Define Quality Assurance.
Ans: Quality Assurance is a broad range of concepts that contains all the matters that individually or collectively affect the Quality of a product. QA mainly concentrated on planning and documenting the procedures to ensure Quality.
Q.2 What is Documentation?
Ans: Documentation is all types of written procedures, records, and instructions, Quality control test records with procedures involved in all manufacturing activities of drug products.
Q.3 What are In-process checks?
Ans: In-process checks are checks carried out during an activity to monitor and, where necessary, to adapt the process to ensure that the product conforms to its specifications.
Q.4 During In-process Checks, what will need to be checked/Recorded?
Ans: Recording of various parameters like; 1) Environmental Monitoring 2) Measured values obtained from the process equipment (ex: temperature, RPM.) 3) Measured values obtained from persons (ex: timings, entries.) 4) Process attributes (Ex: weight, hardness, stability.
Q.5 What precautions shall be taken while collecting in-process samples?
Ans: While collecting in-process samples, protect the sample from contamination while sampling (Do not collect samples with bare hands). Use gloves while sampling.
Q.6 What are the factors that influence tablet hardness?
Ans: 1. force applied for compression
2. Binder quantity (More binder quantity, more hardness)
3. Presence of moisture in granules.
Q.7 If the leak test falls during In-process checks, what needs to be done?
Ans: Immediately stop the packing process and check for:
1. Sealing temperature
2. Check knurling quality and change in printed foil.
3. Check & quarantine the isolated quantity of packed goods from the last leak test passed during in-process.
4. Collect random samples & do a retest.
5. Blisters from the leak test passed containers shall allow going further, and the rest must be de-blistered/ Defoil accordingly.
Q.8 What needs to be checked during AHU validation?
Ans: During AHU validation, the following tests shall be carried out:
1) Air velocity & number of air changes
2) Airflow pattern (visualization)
3) Differential pressure, temperature, and RH
4) Static condition area qualification
5) Dynamic condition qualification
6) Non-viable count
7) Microbial monitoring
8) Area recovery and power failure study
Quality Assurance Interview Questions Related to Documentation
Q.9 What Is a Change Control?
Ans: Change Control is a general term describing the process of managing how changes are introduced into a controlled System. Into validation, implies how changes to the validated system are made. Change control is needed to demonstrate to regulatory authorities that after system modifications, validated systems remain under Control after system changes.
Q.10 What Is SOP?
Ans: A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is a specific type of document that describes how to perform a particular task or operation in a step-by-step outline. To ensure that tasks are conducted consistently and appropriately, everybody in an organization must follow the same procedures.
Many organizations have a broad range of SOPs that illustrate how to execute various tasks. In many companies, technicians, and operators are trained in how to follow individual SOPs and their training record specifies the SOPs they are trained on and are authorized to use.
Q.11 Tell about the content of the SOP
Ans: 1. Objective or Purpose/Aim
2. Scope
3. Responsibility
4. Procedure
5. Precautions
6. Annexure
7. Abbreviations
8. Reference
9. Revisions History
Q.12 How do stability studies?
Ans: These are necessary for developing pharmaceutical products. The influence of environmental factors (e.g., light, humidity, temperature.) on active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) or pharmaceutical ingredients (API) may be evaluated.
Q.13 Expand BMR and BPR
Ans: BMR – Batch Manufacturing Record, prepared as a written file during the Manufacturing of a product by writing, and Recording step-by-step manufacturing process, and details about batch recorded here. For every BMR, BPR is to be held for further packing records. BPR depends on packaging operation.
Related: Difference between BMR/eBMR/eBPR
Q.14 Difference between validation and calibration?
Ans: Validation provides written evidence to ensure that a particular method or operation continuously develops a product with predetermined requirements and quality credits. It is performed according to the validation protocol.
Calibration denotes that Equipment produces the values in specified limits by comparing the values produced by a standard. It Is done according to the calibration SOP.
Q.15 What is a Change Request?
Ans: Change Control is a general term that describes the process of managing the implementation of changes in a controlled system that is controlled by the change request. control system into validation means how changes are made to the validated system. Change Control is made to demonstrate to the Regulatory authority, the reason that the validated system remains under Control after the system change. Change Control systems are a favorite target of regulatory auditors because they vividly demonstrate an organization’s capability to Control systems.
Q.16 What is 21 CFR part 11?
Ans: Title 21 CFR Part 11 of the Code of Federal Regulations deals with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines on electronic records and electronic signatures in the United States.
Q.17 Tell any five countries with their regulatory authorities.
Ans: India Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
USA – United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA).
UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
Japan- Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare (MHLW).
Australia- Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
Common IPQA Interview Questions
Q.18 What position of the oblong tablet to be placed in the hardness tester to know the hardness
Ans: It should be lengthwise because its breakage probability is higher in this position.
Q.19 Why do we calibrate an instrument at a particular interval?
Ans: because it can be possible for instruments to drift out of accuracy after qualification. So it needs to requalify the instrument at a specific time interval.
Q.20 What checks shall be carried out during the calibration of the Disintegration Test apparatus?
Ans: 1. Strokes number per minute. It shall be a 29-32 cycle per minute.
2. Temperature by using probes and a standard thermometer. It shall be 37±1°C
3. Traveling distance by the basket. It shall be 53-57 mm.
Q.21 Why is positive pressure kept in the corridor, not in the process area?
Ans: The different pressure gradients are essential at different locations to avoid cross-contamination of a product through the air.
Q.22 Recommended storage condition for empty hard gelatin capsule
Ans: It should be 15-25°C and 35-5/% RH.
Q.23 What shall be the DT Temperature recommendation for dispersible tablet
Ans) 25±1°C (IP) and 15-25°C (BP)
Q.24 Difference between validation and calibration?
Ans: Validation provides written evidence to ensure that a particular method or operation reliably develops a product with predetermined requirements and quality credits. It is performed according to the validation protocol.
Calibration denotes that Equipment produces the values in specified limits by comparing the values produced by a standard. It Is done according to the calibration standard operating procedure.
Q.25 Tell the time required for long-term and accelerated stability testing.
Ans: long term study 12 months
Accelerated stability for six months.
Q.26 What is SISPQ?
Ans: Safety, integrity, strength, purity, and Quality.
Q.27 Which Fluorescence material is used in BIN Washing while PQ?
Ans: Riboflavin
Q.28 Which class of Area is Required for Tablets and Capsule Manufacturing?
Ans: Class D
Q.29 What is positive pressure?
Ans: The atmospheric pressure is higher than the immediate surrounding areas, usually measured in inches of water or Pascal.
Q.30 What is the schedule- M?
Ans: schedule- M is the Good Manufacturing Practices and its Requirements of premises of the plant, waste disposal, and Equipment.
GMP is divided into two separate parts:
GMP I for Factory premises
GMP II For plant and Equipment.
Q.31 What is the Deviation?
Ans: A deviation is an unexpected event that accrues during the ongoing operation/ activity/ Documentation/ entries at any stage of receipt, storage and Manufacturing, analysis and distribution of drugs products/Intermediate/Raw materials/ packing materials. The deviation is to be reported as and when events occur and to be investigated for impact analysis.
Q.32 What is VMP?
Ans: VMP Means Validation master plant. It is about brief information about the Qualification, Validation, and calibration of Equipment, instruments, and systems. VMP is a type of document providing information on the company’s Validation work program. Responsibility related to VMP should be stated.
Related: Technical pharmaceutical interview questions/answers
Q33. What are Market Complaints?
Ans: A complaint includes any expression of dissatisfaction with a marketed product or service. Any written or genuine verbal communication received directly from a customer, retailer, distributor, healthcare professional, regulatory agency, patient (consumer), or field staff regarding the safety, identity, strength, purity, quality, shortages, or any other such complaint should be treated as a market complaint.
Q.34 What is a Product recall?
Ans: Product recall is the Removal or correction of marketed products for reasons relating to deficiencies in Quality, safety, or efficacy, including labeling considered to violate the laws.
Q.35 Vendor Qualification?
Ans: New Vendor: Manufacturer identified by Formulation Development or purchase department as a manufacturer supplying a specific material from a specific manufacturing site.
Approved Vendor: Manufacturer of raw material, primal, and printed packaging material, approved by QA to supply specific material from a specific site, based on the cGMP.
Q.36 Cleaning Validations?
Ans: DEFINITION: Cleaning Validation is the documented evidence that an approved cleaning procedure will provide Equipment suitable for processing medicinal products.
Q.37 What is Annual Product Quality Review (APQR):
Ans: Annual Product Quality Review (APQR) is a documented regular periodic or rolling quality review of all licensed medicinal products. It verifies the consistency of the existing manufacturing process, highlights any trends, and identifies product and process improvements or weaknesses for licensed medicinal products. It assesses the appropriateness of current specifications for both starting materials and finished products.
Q.38 What is the limit for “individual unknown Impurity” in API as per ICH Q2A?
Ans: The limit of the “Any individual unknown Impurity” is not more than 0.1%
Q.39 What are the class-1 solvents as per ICH Q3C?
Ans: Benzene – 2
Carbon tetrachloride -4ppm
1, 2 Dichloroethane – 5ppm
1, 1 Dichloroethene – 8ppm
1, 1, 1 -Trichloroethane-1500 ppm
Q.40 Different ICH guidelines
Ans:
Q.41 What is the specific gravity of Methylene chloride?
Ans: The specific gravity of Methylene chloride is 1.308 gm/ml
Q.42 Suppose the Area is class 100000, then what are the maximum light and sound levels as per guidelines?
Ans: light level: not less than 300 lux.
Sound level: it should not be more than 80 decibels.
Related: Lux/Light intensity requirements
Q.43 What is the instrument name, which is used for measuring vacuum during high vacuum distillation?
Ans: Macleod gauge
Q.44 Is the cGMP requirement only for personnel in Manufacturing?
Ans: No, this requirement is for every employee of the organization who must know relevant cGMP requirements in his/her Area.
Q.45 Why do we conduct the training?
Ans: It brings awareness and helps employees to become competent.
Q.46 India belongs to which Climate Zone?
Ans: India comes under Climate Zone III (Known as the Hot, dry Zone) and Zone IVb (known as Hot/Higher humidity)
Q.47 What is force degradation or stress testing:
Ans: Force degradation is also known as stress testing, and a drug is degraded Forcefully by applying artificial methods.
It helps to know about Impurities that develop during the storage of drug products in various environmental conditions. Forced degradation study depends upon the product and the type of dosage form. Solid, liquid, and injection have different procedures for the stress study.
Q.48 Explain Qualifications and their flow
Ans: Design Qualifications, installation Qualifications, Operational Qualifications, and Performance Qualifications. Flow=URS>> FAT>>SAT>>DQ>>IQ>>OQ>>PQ.
Q.49 What is a Critical Quality Attribute?
Ans: it is chemical, physical, biological, and microbiological characteristics that should be under limits and range to ensure the Quality of the products.
Q.50 What is OOS (Out of Specification)?
Ans: A result that falls outside established acceptance criteria established in official compendia and by company documentation.
OR
Out of specification is the comparison of one result versus predetermined specification criteria.
Example of OOS (Out of Specification):
The specification limit for the assay is 90.0-110.0 % w/w of the label claim.
For a selected batch, the result obtained is 85.2 % w/w – This result is out of the specification limit, which is often called OOS.
Q.51 What is OOT (Out of TREND)?
Ans: Results of a drug substance of a selected batch, which is within the specification limit but a similar result compared to other batches of a similar drug substance, falling outside the typical results of all compared batches.
Or
specification results may be within limits but show a significant change from the historical results.
Example of OOT (Out of TREND):
The result obtained 95.8 % w/w. Although the results are well within the specifications, we should always compare the results with the previous batch’s trend. If we found the typical value of the trend as 99.0 % w/w, then this batch result (95.8 % w/w) is named out of trend.
Quality Assurance Interview Questions related to the processing Area?
Q.52 What is relative humidity?
Ans: it is the ratio between the amount of water vapor in a particular air volume and at provided temperature. The maximum amount of water vapor that the air can possess.
Q.53 If the temperature or RH of the Area goes out of the limit, what action is to be taken?
Ans: immediately stop the line, and inform the responsible department to raise the maintenance requisition slip. Ensure that all the intermediate materials are correctly covered.
Q.54 How to stop cross-contamination in an area?
Ans: By ensuring to follow proper gowning procedure and material transfer procedure and controlled staffing movement in the Area, maintaining Differential pressure is also essential to controlled cross-contamination.
IPQA Pharma Interview Question:
Q.55 What is process validation?
Ans: As per EMA Definition process validation is “documented evidence that of a method, operated within established parameters, that can be performed effectively and reproducibly to provide a medicinal product meeting as per its predetermined specifications and quality attributes.”
USFDA Definition Process validation is “The evaluation of data and collection, from the process design stage throughout the production stage, to consistently delivering a quality product” based on established scientific evidence.
Q.56 Consistent with regulatory guidelines (USFDA), what are the stages of process validation?
Ans: Process validation involves a series of activities happening over the lifecycle of Drug products and processes. There are three stages for process validation activities.
Stage 1 — Process Design: The commercial manufacturing process is defined based on knowledge gained through development and scale-up activities.
Stage 2 — Process Qualification: During this stage, the method design is evaluated to determine if the method is capable of reproducible commercial manufacturing.
Stage 3 — Continued Process Verification: Ongoing assurance is gained during routine production that the method remains in a state of Control.
Q.57 Tell How many batches were taken for the process validation?
Ans: The EMA draft guideline states “a minimum of three consecutive batches,” with justification to be provided (there are some exceptions to the current statement).
The USFDA guidance states that the number or quantity of batches must be sufficient to supply statistical confidence in the method. It is a subtle but essential distinction in the approaches.
Q.58 Explain the strategy for process validation of solid dosage forms.
Ans: The use of different lots of raw materials should be included. i.e., active drug substance and major excipients.
- Batches should be run serial and on different days and shifts (the latter condition, if appropriate). Batches should be manufactured within the Equipment and facilities designated for eventual commercial production.
- Critical process variables should be set within their operating ranges and will not exceed their upper and lower control limits during process operation. Output responses should be within the finished product specifications.
- Failure to satisfy the wants of the Validation protocol regarding process input and output control should be subjected to process requalification.
Q.59 What is the Validation Protocol?
Ans: A written plan of action stating how process validation will be conducted; it will specify who will conduct the various tasks and define testing parameters; sampling plans, testing methods, and specifications; will specify the product and its characteristics And Equipment to be used.
It must specify the number of batches and acceptance criteria to be used for validation studies; and who will sign/approve or Disapprove the conclusions derived from such a scientific study.
Q.60 What should be processed validation protocol content?
- General information
- Objective
- Background/Pr- validation Activities, Summary of development and tech transfer (from R&D or another Site) activities to justify in-process testing and controls; any Previous validations.
- List of Equipment and their qualification status
- Facilities qualification
- Process flow charts
- Manufacturing procedure narrative
- List of critical processing parameters and necessary excipients
- Sampling, tests, and specifications
- Acceptance criteria
Q.61 What should be the blend sample size in In-process validation studies?
Ans: It is a 1x – 3x dosage unit range on a case-to-case basis. As per USFDA guidance, sampling sizes are often increased from lx -10x with adequate scientific justification.
Q.62 How many sampling points should be considered for collecting blend samples According to USFDA guidance?
Ans: According to USFDA guidance, At least 10 sampling locations are to be considered.
In the case of connective blenders, At least 20 locations are recommended to validate adequately (ex: ribbon blender)
Q.63 What will be the reason for the inside location variance of blend data?
Ans: Inadequacy of blend mix, sampling error, or agglomeration
Q.64 What is the difference between EMA & US guidelines on process validation?
Ans: EMA US Definition “documented evidence that the process, operated within established parameters, can perform effectively and reproducibly to produce a medicinal product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality attributes.”
Definition It is “The evaluation of data and collection, from the process design stage throughout the production stage, to consistently delivering a quality product based on established scientific evidence.” The EMA draft guideline states “a minimum of three consecutive batches,” with justification to be provided (there are some exceptions to the present statement).
The US FDA guidance states that the number of batches must be sufficient to supply statistical confidence in the method. The EMA draft encourages the use of product development activities but is less sanctioned on requirements. The USFDA guidance emphasizes documenting the event phase as a part of PV. The EMA guideline explicitly allows the utilization of CPV to exchange traditional validation efforts.
The US FDA approach does not place a high emphasis on CPV. It requires all three stages of process validation to be fully addressed, regardless of whether contemporary or traditional methods are utilized. The US FDA guidance considers Equipment and process design and equipment qualification as part of the overall process validation effort. The EMA guideline sees the process as independent from Equipment and facility. Currently, the EMA still relies on Annex-15 of the GMP guide for instruction on equipment qualification.
Q.65 During process validation, Why was the hopper challenge study performed?
Ans: A Hopper challenge study was performed to evaluate the effect of vibrations during compression on blend uniformity, a hopper study shall be carried out.
Q.66 What are the critical process variables in the coating?
Ans: Pan RPM, inlet & exhaust temperature, spray rate, gun distance, and air pressure.
Q.67 Why may blend be a critical parameter in tablet manufacturing?
Ans: Less blending will result in a non-uniform distribution of drugs and poor flow, whereas more blending will result in de-mixing leading to a non-uniform distribution of drugs and an increase in disintegration time
Q.68 What is the mess size of the DT apparatus?
Ans: 1.8 to 2.2mm (#10)
Q.69 DT Apparatus Limits/ Tolerance Limits
Ans: Disintegration test apparatus Limits/ Tolerance Limits are as follows:
- Temp. of water bath/Actual observation / Tolerance limit 37-39°C
- Temp. in the beaker/ Actual observation L&R/ Tolerance limit 37±2°C
- No. of strokes/min./4times Actual observation L&R/ Limit 29-32
cycle./min. - Stroke heights/ Actual observation L&R/ Tolerance limit 55 ±2mm.
- Baskets lowermost position/ Actual observation L&R/ 25 mm.
- Sieve Integrity/ Actual observation L&R/ 2.0mm ±0.2mm
Q.70 What is the recommended temperature for checking DT for dispersible tablets?
Ans: 25±1°C as per (IP) and 15 to 25°C as per (BP).
Q.71 Tell pass and fail criteria for DT?
Ans: Repeat the test on 12 additional tablets or units if 1 or 2 units fail to disintegrate. The goal is achieved if 16 out of 18 tablets/capsules disintegrate entirely.
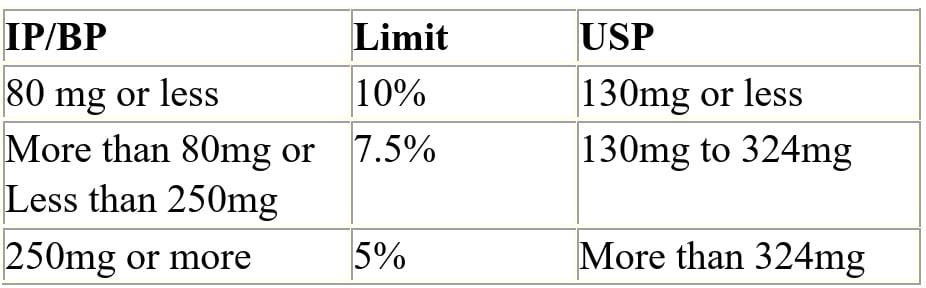
Q.72 Weight variation limits for Tablets?
Ans:
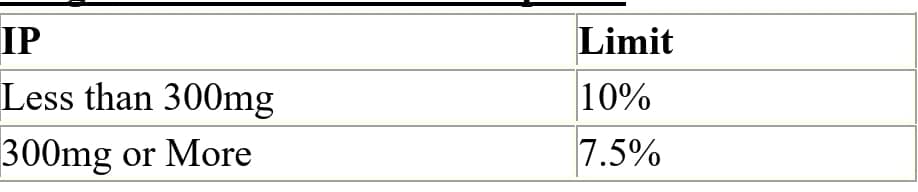
Q.73 Weight Variation Limits for Capsules?
Ans:
Q.74 Metal detector test and Principle with test piece size for Tablets and Capsules
Ans: Principle- Electromagnetic induction principle
Test piece- Tablets – Ferrous (0.3mm), Non-Ferrous (0.3mm), Stainless steel (0.5mm), Plain
Capsule – Ferrous (0.1mm), Non-Ferrous (0.15mm), Stainless steel (0.20mm), Plain
Q.75 Define Clean hold time
Ans: The clean hold time is defined as the time between the completion of cleaning and the initiation of the subsequent manufacturing operation.
Q.76 Define Dirty hold time
Ans: The dirty hold time is defined as the time between the end of the manufacturing operation and the beginning of the cleaning process.
Q.77 Define Campaign Cleaning:
Ans: Campaign Cleaning: Campaign cleaning shall be performed after a series of the same product batches are manufactured with the batch-to-batch cleaning procedure. Campaign cleaning shall be performed if 8 batches of the same product have been processed or 3 days have passed, whichever is earlier
Q.78 Define Batch-to-Batch Cleaning:
Ans: Cleaning shall be performed between batches and subsequent batches, where the previous and next products are the same.
Q.79 Maximum Allowable Residue (MAR):
Ans: Maximum Allowable Residue is an acceptable transferred amount of residue from the previous product to the next product.
Q.80 What are ALCOA and ALCOA++?
Ans: Read Full details about ALCOA and ALCOA++ with examples here
Q.81 Define CAPA with an Example.
Ans: Read about CAPA and its Example here
Q.82 Tells me about Different Quality Risk Management Methodology
Ans:
- Basic risk management facilitation methods (flowcharts, check sheets, etc.)
- Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis (FMECA)
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
- Hazard Operability Analysis (HAZOP)
- Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA)
- Risk ranking and filtering
- Supporting statistical tools
Q.83 Define the Black area
Ans: Non-manufacturing areas, such as warehouses, administration, and workshop comprises the black area. Temperature and R.H. should be controlled as per material specifications in a warehouse storage area.
Q.84 Define Dark gray area
Ans: Areas, where primary packaged products are handled, such as visual inspection of ampoules, vials, blisters, and final packaging operations, comprise the dark gray area. Depending on the product temperature and relative humidity should be controlled.
Q.85 Define Gray Area
Ans: Areas where operations like sampling, dispensing, compounding, and producing solids, semisolids, and liquids for oral use comprise gray areas. These are areas where personnel could come into direct contact with open materials (starting materials, intermediate products, and open primary packaging material).
Q.86 Define Blue Area
Ans: Parenteral bulk preparation takes place in the blue area.
Q.87 Define Green Area
Ans: Parenteral filling operation takes place in green areas.
Q.88 Tell me the types of Sampling
Ans: Random Sampling, Systematic Sampling, and Representative Sampling.
Q.89 Define Random Sampling
Ans: Random Sampling is the sampling taken at random from the whole population of the material. The only requirement of such a random sampling process is that all parts of the population have the same chance of being sampled. e.g., Inactive R.M.
Q90. Define Systematic Sampling
Ans: Systematic Sampling is the sampling collected on the basis of a given geometric or time pattern, i.e., at regular intervals. e.g., Sampling of water
Q91. Define Representative Sampling
Ans: Representative Sampling is the sampling from the various layers & a composite sample is prepared eg. composite samples from the container are sampled.
Q.92 What are the types of different training programs?
Ans: 1. Induction training
2. Job-oriented training
3. cGMP training
4. Ongoing training
Q.93 What are the classifications of residual solvents?
Ans: Residual solvents are classified into three classes based on the possible risk to human health:
Class-I (Solvents to be avoided)
Class-II (Solvents to be limited)
Class-III (Solvents with low toxic potential)
Q.94 What is the difference between Responsibility and Accountability?
Ans: Responsibility: Personnel directly associated with the implementation of the procedure
Accountability: Person directly associated with the implementation of the system under
which the procedure falls.
Q.95 Why is nitrogen gas used in the manufacturing area at room temperature, and why not another gas?
Ans: Because nitrogen is chemically less reactive and does not react with other elements at ordinary temperatures. It is due to strong bonding in its molecules.
Q.96 What are the different types of cleanings?
Ans: There are three types of cleanings:
● Batch to Batch cleaning
● periodically cleaning
● Product changeover cleaning
Q.97 What is the Expiry date & Re-test date?
Ans: Expiry date: The date placed on the container/labels of an API designates the time during which the API is expected to remain within established shelf life specifications if stored under pre-defined conditions, and after that, it should not be recommended for use.
Re-test date: The date when a material should be re-examined/Resampled to ensure that it is still used for product manufacturing. The time period during which the drug substance/molecules are expected to remain within their specifications as per COA and thereafter can be used in the manufacturing, provided that the drug substance has been stored under the defined conditions.
Q.98 What are Contamination and Cross-contamination?
Ans: Read complete details about contamination and cross-contamination here
Q.99 What is the Batch number and batch?
Ans: Batch Number: A unique combination of numbers, letters, and/or symbols that identifies a batch (or lot) and from which the production and distribution history can be determined
Batch: A specific lot of material produced in a process or series of processes in an area, so that it is expected to remain in homogeneous form within given limits.
Q.100 What is Quarantine?
Ans: The status of materials isolated physically or by other effective means pending a decision on their subsequent approval or rejection.
Q.101 What is the definition of Critical Process Parameters?
Ans: A process parameter whose variability has an impact on a critical quality attribute and therefore should be monitored or controlled to ensure the process produces the desired quality.
Note: Please keep visiting this page to get regular updates on Quality Assurance Interview Questions in the pharmaceutical field. This will help you stay informed and up-to-date with the latest information.

Naresh Bhakar is the Founder and Author at Pharmaguddu.com, bringing his extensive expertise in the field of pharmaceuticals to readers worldwide. He has experience in Pharma manufacturing and has worked with top Pharmaceuticals. He has rich knowledge and provides valuable insights and data through his articles and content on Pharmaguddu.com. For further inquiries or collaborations, please don’t hesitate to reach out via email at [email protected].

thanks you very much for provided
Thank you for providing Very good content & useful data on interview questions related to quality assurance.
Thank you so much for providing this.
Thank you so much for QA related Interview Questions
Thank you for very informative content.